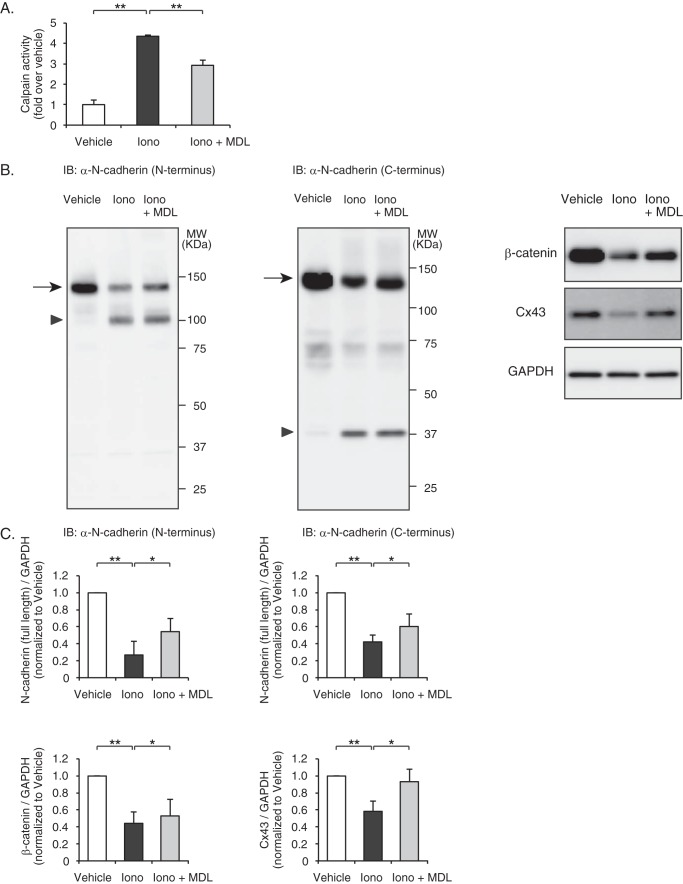
FIGURE 6.
Calpain-mediated degradation of N-cadherin and down-regulation of intercalated disc proteins in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes. A, ionomycin-induced calpain activation in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes. Cells were pretreated with MDL28170 (10 μm) and stimulated with ionomycin (10 μm) for 10 min, and calpain activity was determined by a luminescent assay. Experiments were repeated three times in triplicate, and data are shown as -fold induction over vehicle control (mean ± S.E.). Iono, ionomycin; MDL, MDL28170. **, p < 0.01. B, immunoblot (IB) analysis of N-cadherin, β-catenin, and Cx43 in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes. Besides the full-length N-cadherin (arrows), the degraded N-terminal fragments (arrowhead) and C-terminal fragments (arrowhead) were detected by anti-N-cadherin antibody raised against the extracellular domain and intracellular domain of N-cadherin, respectively. C, quantitation of the N-cadherin (N terminus)/GAPDH (n = 6), N-cadherin (C terminus)/GAPDH (n = 7), β-catenin/GAPDH (n = 3), and Cx43/GAPDH (n = 4) are shown as bar graphs (right panel). Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.