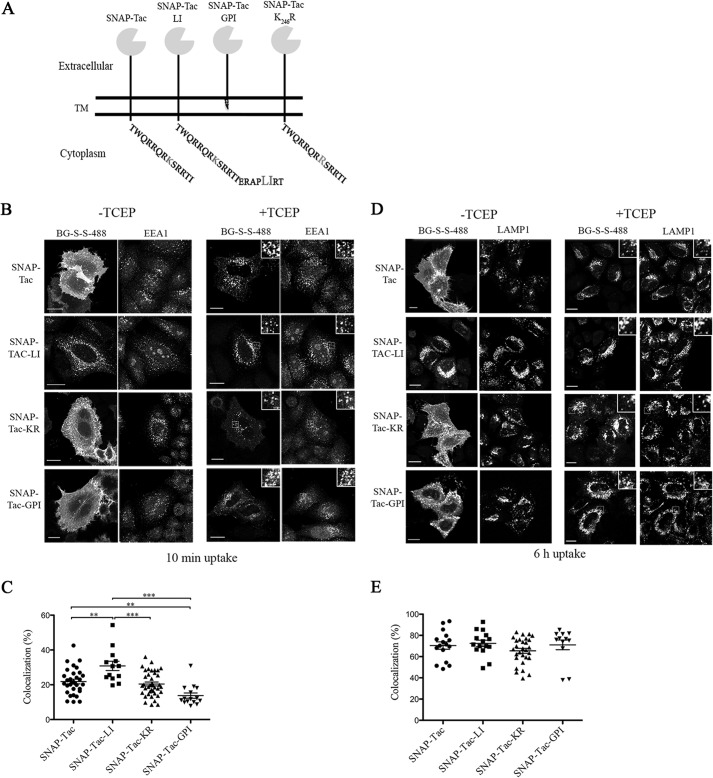
FIGURE 1.
Endocytosis of SNAP-Tac chimeras. A, schematic representation of various SNAP-Tac constructs. TM, transmembrane domain. B, HeLa cells expressing SNAP-Tac fusion proteins were labeled with BG-S-S-488 at 4 °C for 30 min and then incubated for 10 min at 37 °C. Cells were not treated (left panels) or treated (right panels) with 10 mm TCEP for 2 min at 37 °C to remove the surface label and then fixed. After fixation, cells were immunolabeled with antibodies to EEA1 followed by species-specific secondary antibodies to detect EEA1-positive endosomes. The insets illustrate colocalization between internalized SNAP-Tac proteins and EEA1. C, colocalization analysis between SNAP-Tac chimeras and EEA1. One-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's post hoc multiple comparison test was used to compare colocalization values. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. **, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001. D, HeLa cells expressing SNAP-Tac fusions were labeled with BG-S-S-488 at 37 °C for 1 h and then transferred to media containing 25 mm NH4Cl to block lysosomal degradation. After 6 h, cells were treated or not with 10 mm TCEP and fixed as above. After fixation, cells were immunolabeled with antibodies to Lamp-1 followed by species-specific secondary antibodies to detect Lamp1-positive lysosomes. The insets illustrate colocalization between internalized SNAP-Tac proteins and Lamp1. E, one-way analysis of variance was used to compare colocalization values between SNAP-Tac chimeras and Lamp-1 as above. No significant colocalization differences were observed between various constructs. Bars, 10 μm.