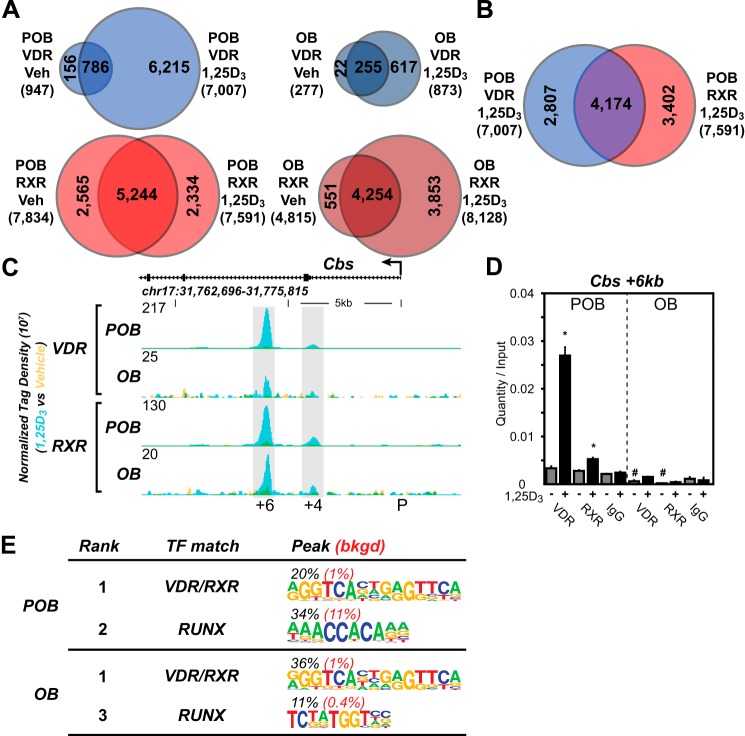
FIGURE 2.
Delineation of the VDR cistromes in POBs and OBs. A, Venn diagram depiction of replicate normalized VDR- (blue) and RXR (red)-binding sites in vehicle (Veh) and 1,25(OH)2D3 (1,25D3)-treated undifferentiated (POB) cells (left) and differentiated (OB) cells (right). B, overlapping Venn diagrams for VDR and RXR in the POB-treated cells from the 1,25(OH)2D3 condition. C, ChIP-seq tag density tracks for the Cbs gene locus for VDR and RXR binding (Veh, yellow; 1,25(OH)2D3, blue; overlap, green) in the POB and OB cells. Genomic location and scale are indicated, and maximum height of tag sequence density for the data track is indicated on the y axis (normalized to input and 107 tags). Gene transcriptional direction is indicated by an arrow and exons by boxes. Peak regions of interest are highlighted by gray boxes, and their distance from TSS (P, promoter) is indicated below. D, ChIP-qPCR analysis of Cbs +6-kb peak region. Data displayed as quantitation normalized to ChIP input ± S.E. *, p < 0.05, 10−7 m 1,25(OH)2D3 (+) versus vehicle (−) within ChIP antibody by Student's t test. #, p < 0.05, POB versus OB by Student's t test. E, de novo over-representation analysis of VDR 1,25(OH)2D3 peak sequences and matching transcription factor-binding sites found through HOMER. Abundance shown as percentage (black) compared with 50,000 GC content matched sequences (red).