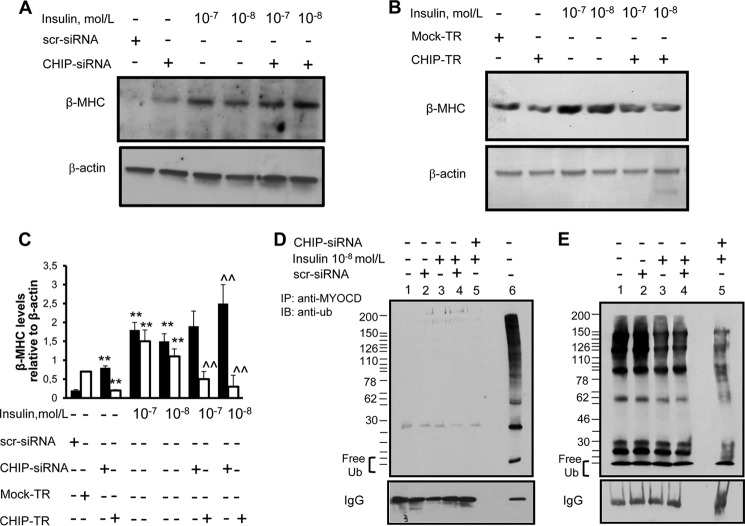
FIGURE 4.
Insulin down-regulation of ubiquitinated CHIP and modulation of myosin heavy chain-β in response to overexpression and silencing of CHIP. A, β-MHC induction in response to CHIP-siRNAs and/or insulin. Canine cardiac myoblasts were transfected with a pool of three different CHIP siRNAs oligonucleotides or a scrambled (scr) siRNA (negative control), and treated with insulin (10−8–10−7 mol/liter) for 24 h. B, β-MHC repression in response to CHIP overexpression. Canine cardiac myoblasts were either mock-transfected (mock-TR, negative control) or transfected with CHIP (CHIP-TR), then treated with 10−8 mol/liter insulin (10−8-10−7 mol/liter) for 24 h. Following treatments, the expression of β-MHC was detected by immunoblotting. Blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. C, results of scanning densitometry (n = 3 independent experiments) expressed as a ratio of β-MHC to β-actin in three different immunoblots represented in panels A and B. Columns and bars represent the mean ± S.D. (**, p < 0.01, versus untreated cells; ^^, p < 0.01 versus insulin-treated cells). D–E, insulin-mediated decrease of CHIP ubiquitination. Canine cardiac myoblasts were transfected with a pool of three different CHIP siRNA oligonucleotides or a scrambled siRNA (negative control), and then treated with insulin (10−8 mol/liter) for 24 h. Proteins were immunoprecipitated with an anti-myocardin antibody and subjected to ubiquitination reactions (panel D, lane 6 and panel E). Panel D, lanes 1–5 shows control experiments with immunoprecipitates incubated in 50 μl of control buffer. Reactions were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, followed by immunoblotting with anti-Ub antibody (panels D and E). Here shown is a blot representative of three independent experiments.