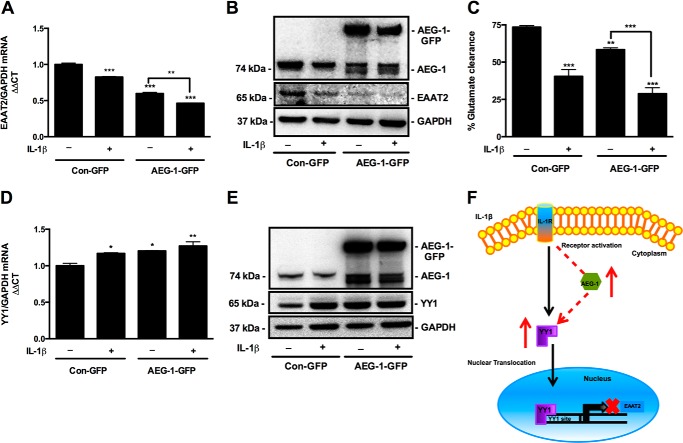
FIGURE 7.
AEG-1 overexpression in astrocytes reduced EAAT2 levels and glutamate clearance by regulating YY1 expression. Astrocytes transfected with AEG-1-GFP or Con-GFP constructs were treated with IL-1β (20 ng/ml) for 24 h, and changes in EAAT2 mRNA and protein levels were analyzed by real time RT-PCR and immunoblotting, respectively. A, AEG-1 overexpression alone significantly reduced EAAT2 mRNA levels and further exacerbated the IL-1β-mediated loss in EAAT2 expression (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). B, AEG-1 overexpression alone significantly reduced EAAT2 protein levels and further augmented the IL-1β-mediated decrease in EAAT2 protein levels. C, effect of AEG-1 overexpression on glutamate clearance by astrocytes was studied by fluorometric assay. AEG-1 overexpression alone significantly reduced glutamate clearance and further augmented the IL-1β-mediated impairment in glutamate clearance (***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05). D and E, AEG-1 regulation of EAAT2 was analyzed by real time RT-PCR and immunoblotting for YY1. AEG-1 overexpression alone and in combination with IL-1β significantly elevated YY1 mRNA and protein levels (**, p < 0.01). GAPDH was used as a normalizing control for mRNA and protein quantification. Representative data from two individual donors are shown. F, proposed mechanism of AEG-1 regulation of EAAT2. IL-1β activates the NF-κB pathway to induce AEG-1 expression, which further up-regulates YY1 expression leading to EAAT2 down-regulation.