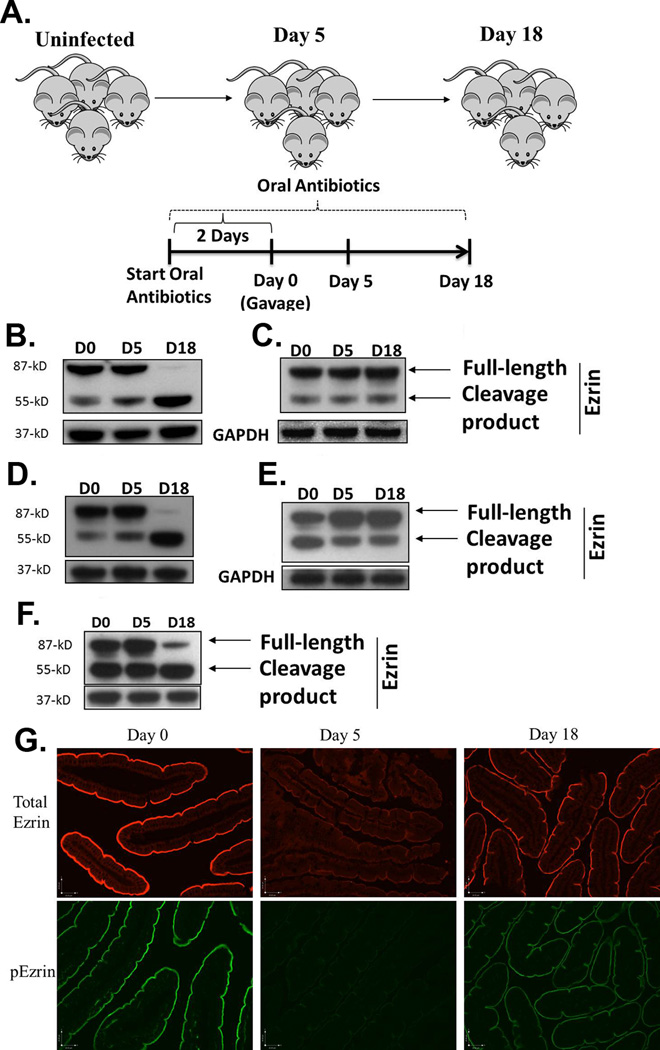
Figure 1.
Post-translational regulation of ezrin following gut infection. The experimental protocol for infecting mice with both strains of G. duodenalis is depicted in (a). Mice were maintained on neomycin, vancomycin and ampicillin throughout the experiment to facilitate infection with either strain of parasite. WT (b), SCID (c), β2m−/− (d), and CD4−/− (e) mice were infected with the GS strain of G. duodenalis and jejunal homogenates were examined for post-translational modifications in ezrin using Western blots. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Each figure is representative of 4 mice / time point. Ezrin was also analyzed following infection of WT C57BL/6 mice with the WB strain of the parasite (f). Using paraffin-embedded tissue and IF, the localization of total ezrin (upper panel) and phosphorylated ezrin (p-ezrin, lower panel) was also determined in the intestines of mice infected with the GS strain of the parasite for 0, 5 or 18 days (g). Each panel represents 4 mice/time point.