Figure 5.
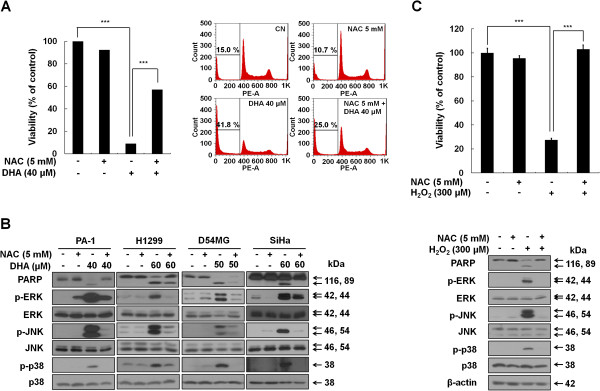
Excessive ROS is associated with activation of MAPKs and subsequent apoptosis induced by DHA. (A) DHA-induced ROS production is required for apoptosis. PA-1 cells were exposed to 40 μM DHA in the presence or absence of 5 mM NAC for 12 h. Left, cell viability was determined by the MTT assay. ***, P < 0.001. Each bar represents the mean of three determinations repeated in three separate experiments. Right, cells were collected to examine the percentage of cells in Sub-G1 phase by flow cytometry analysis. Samples were analyzed using FlowJo software. (B) NAC blocks the DHA-induced MAPKs activation. PA-1, H1299, D54MG and SiHa cell lines were incubated for 1 h with or without 5 mM NAC before exposure to the indicated doses of DHA for and 24 h (12 h in case of PA-1 cells). After cell lysis, PARP and MAPKs protein levels were examined by western blot analysis. (C) Apoptosis and MAPK activation in response to exogenous ROS, hydrogen peroxide. PA-1 cells were pretreated with or without 5 mM NAC for 1 h, followed by 300 μM hydrogen peroxide exposure for 12 h. Cell viability and the expression levels of cleaved PARP and MAPK were assessed by MTT assays (upper) and western blot analysis (lower). ***, P < 0.001.
