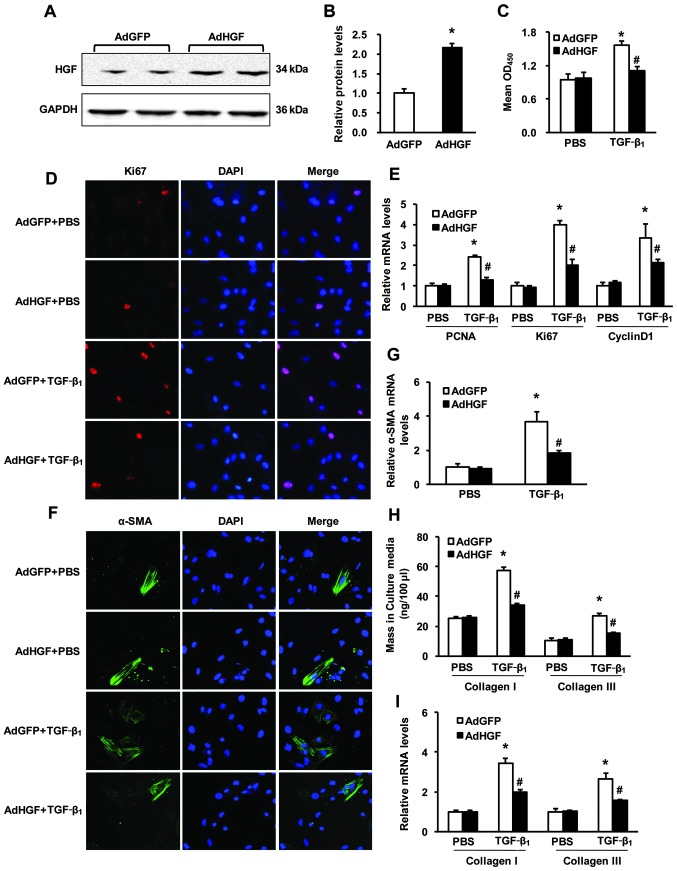
Figure 4.
Overexpression of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) in cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) attenuates transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-induced proliferation, transformation and secretory function. (A and B) HGF protein levels in CFs infected with AdGFP or AdHGF; (A) representative western blots; (B) quantitative results. *P<0.05 vs. AdGFP. (C) The CCK8 assays results indicated that the proliferation of CFs was suppressed by infection with AdHGF following stimulation with 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 48 h. (D) Repesentative images from immunofluorescence staining of Ki67 in CFs infected with AdGFP or AdHGF and stimulated with 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 48 h (red, Ki67; blue, nuclear). (E) The relative mRNA levels of PCNA, Ki67, and cyclin D1 in samples from CFs of the indicated groups. (F) Repesentative images from immunofluorescence staining of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in CFs infected with AdGFP or AdHGF and stimulated with 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 48 h (green, α-SMA; blue, nuclear). (G) Relative mRNA levels of α-SMA in CFs of the indicated groups. (H) Collagen I and III protein secretion in the culture medium of the indicated groups determined by ELISA. (I) Relative mRNA levels of collagen I and III in the CFs of the indicated groups. *P<0.05 vs. AdGFP/phosphate-buffered saline (PBS); #P<0.05 vs. AdGFP/TGF-β1. Three independent experiments were performed.