Figure 2.
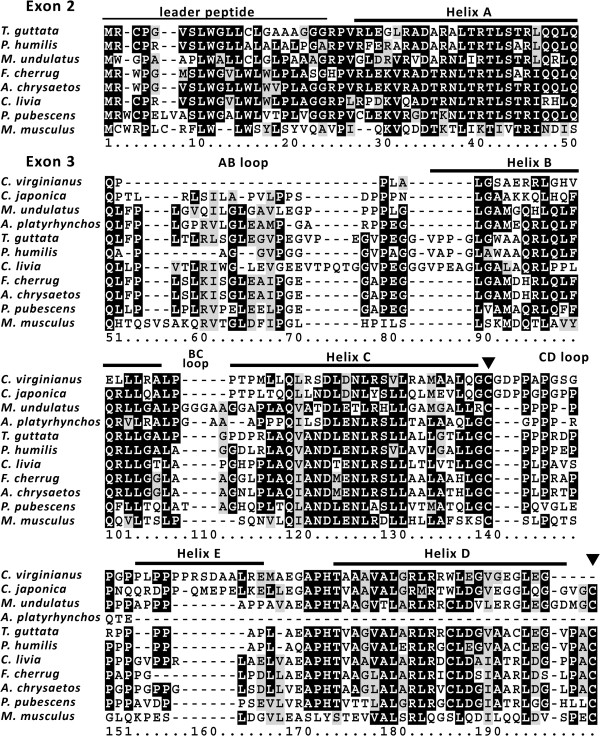
The amino-acid sequence of mouse leptin ( Mus musculus , [GenBank: NP_032519]) was aligned with leptin and LEP -like sequences of birds identified in the WGS and SRA databases: zebra finch ( Taeniopygia guttata , [GenBank: AFK25168]); Tibetan ground tit ( Pseudopodoces humilis , [GenBank: HG425120]); budgerigar (Melopsittacus undulates, [GenBank: AHZ86931]); falcon ( Falco cherrug , [GenBank: HG425122]); golden eagle ( Aquila chrysaetos Canadensis , derived from [GenBank: JDSB01143511, SRR1016445.84242652, SRR1016445.37770192, JDSB01163119, SRR1017148.40189562]; dove ( Columba livia [GenBank: HG797022]); downy woodpecker ( Picoides pubescens , derived from [GenBank: JJRU01076739]); northern bobwhite quail ( Colinus virginianus , derived from [GenBank: AWGU01372785]); Japanese quail ( Coturnix japonica , derived from [GenBank: ERR125582.247893.2, DRR002300.424669919.1, DRR002301.19253882.1, DRR002301.124106485.1, DRR002301.44847625.1]); and the mallard duck ( Anas platyrhynchos , derived from [GenBank: SRR040307.6134664, SRR797835.67134665.2, SRR040316.4927613, SRR797835.67134665.1]). Dashes indicate gaps introduced by the alignment program. Identical and similar amino-acid residues in at least three or six sequences are indicated by a black and gray background, respectively. White boxes indicate non-conservative amino-acid changes between the proteins. The signal peptide and structural elements, helixes and loops [28] are denoted above the alignment. The two conserved cysteines forming a lasso knot [30] are indicated by black arrowheads. Duck’s genomic sequence was confirmed using previously described procedures [28]; DNA was extracted from frozen mallard duck purchased from a local husbandry (Levin, Kfar Baruch, Israel) and nucleotide sequence was determined by capillary sequencing of the 81 bp product amplified using PCR primers (F, 5′-CAGCTTTTCCAGCGCGTC-3; R, 5′-GAGGTTCTCCAGGTCGCTTA-3′).
