Figure 6.
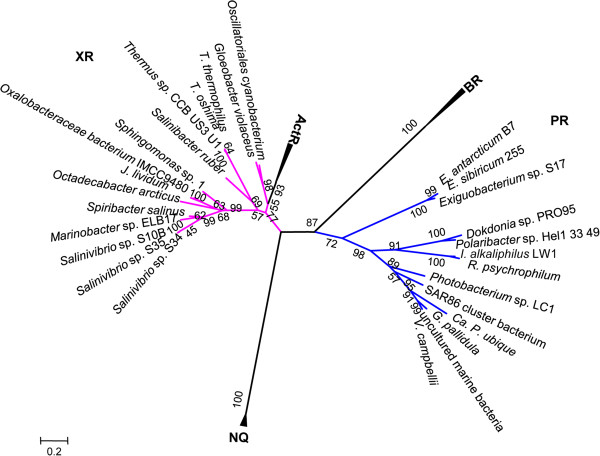
Phylogenetic relationships among microbial rhodopsins. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method [89]. The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 12.05461219 is shown. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the JTT matrix-based method [90] and are in the units of the number of amino acid differences per site. The rate variation among sites was modeled with a gamma distribution (shape parameter = 2.4). The analysis involved 38 amino acid sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. PR, proteorhodopsin (blue); XR, xanthorhodopsin (pink); NQ, NQ rhodopsin; BR, bacteriorhodopsin; ActR, actinorhodopsin.
