Table 1.
Examples of drugs repurposed for use against parasitic protozoal diseases.
| Drug | Structure | Initial use(s) | Repurposed use(s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clindamycin | 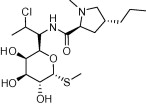 |
Anti-bacterial (e.g. acne) | Malaria – slow acting blood schizontocidal agent; used in combination with fast acting antimalarials; Toxoplasmosis | Miller et al. (1974), Christian and Krueger (1975), Montoya and Liesenfeld (2004) |
| Doxycycline | 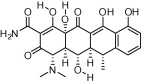 |
Broad-spectrum bacteriostatic agent | Malaria; causal prophylactic (liver stage) and slow acting blood schizontocidal agent; used with fast acting antimalarials | Tan et al. (2011) |
| Co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) | 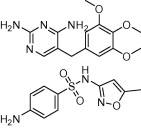 |
Urinary-tract infection, otitis media, shigellosis, and P. carinii pneumonia | P. falciparum malaria in non-pregnant adults and children; dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor; toxoplasmosis | Gleckman et al. (1979), Montoya and Liesenfeld (2004), Manyando et al. (2013) |
| Elfornithine (DFMO) | 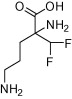 |
Antitumour agent/P. carinii infection in AIDS patients/hirsutism | Human African sleeping sickness – effective against T. b. gambiense but not T. b. rhodesiense | Abeloff et al. (1986), Paulson et al. (1992), Hickman et al. (2001), Shapiro and Lui (2001), Burri and Brun (2003), Kennedy (2008, 2013), Casero and Woster (2009), Simarro et al. (2011, 2012) |
| Miltefosine | 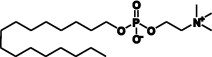 |
Skin metastases (breast cancer) | Vischeral leishmaniasis | Smorenburg et al. (2000), Paladin Labs Inc (2010), Dorlo et al. (2012) |
| Paromomycin | 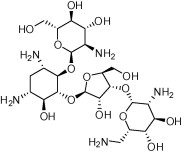 |
Antibiotic; acute and chronic intestinal amebiasis; adjunctive management of hepatic coma. | Parenteral treatment of visceral leishmaniasis; cutaneous leishmaniasis | Ben Salah et al. (2013) |
| Amphotericin B (AmBiome structure shown) | 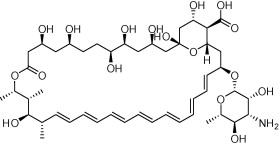 |
Antifungal infections such as aspergillosis, cryptococcosis, North American blastomycosis, systemic candidiasis, histoplasmosis, and zygomycosis | Visceral leishmaniasis; AmBD now superseded by liposomal formulations of amphotericin B such as AmBiome (structure shown) | Meyerhoff (1999), Hu et al. (2003), Ostrosky-Zeichner et al. (2003), Sundar and Chakravarty (2010) |
| Sulphadiazine | 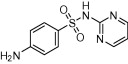 |
Bacterial infections (e.g. streptococcal and staphylococcal infections); topical use against gram −ve and +ve bacterial infections in burns victims | Used in combination with pyrimethamine for prevention and treatment of toxoplasmosis | British Medical Journal (1942), Coloviras et al. (1942), Leport et al. (1988), Guerina et al. (1994), Montoya and Liesenfeld (2004), Rorman et al. (2006) |
| Spiramycin |  |
Antimicrobial (gram-positive organisms) | Congenital toxoplasmosis | Desmonts and Couvreur (1974a), Couvreur et al. (1988), Descotes et al. (1988), Robert-Gangneux and Darde (2012) |
