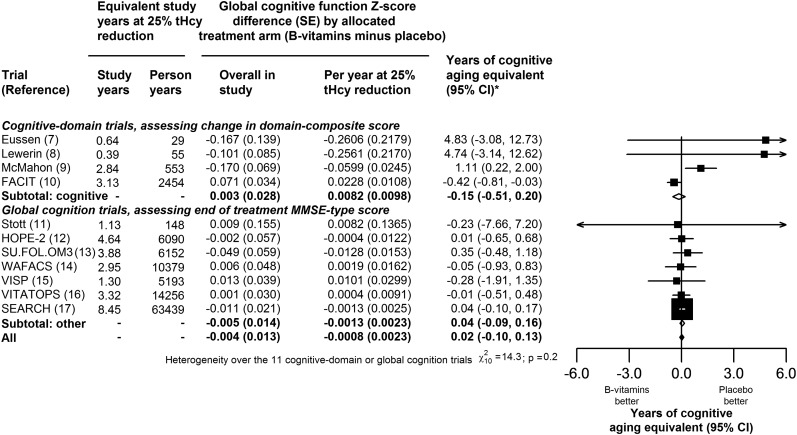
FIGURE 3.
Effects of B vitamins on cognitive aging in all available trials per year at a 25% reduction in homocysteine. The z score differences and their 95% CIs are provided for the domain-composite global cognitive function score in each cognitive-domain trial and for the MMSE-type global cognitive function score in the other trials. The years of cognitive aging equivalent and their 95% CIs are also provided for individual trials and their totals. The years of cognitive aging equivalent were determined on the basis of a 0.054/y reduction in the cognitive domain trial score and a 0.036/y reduction in the global cognition trial score. * indicates that the age association was based on 0.054 per year reduction in domain-composite z score for cognitive-domain trials and on 0.036 per year reduction in MMSE-type cognitive z score. FACIT, Folic Acid and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness; HOPE-2, Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation-2; MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; SEARCH, Study of the Effectiveness of Additional Reductions in Cholesterol and Homocysteine; SU.FOL.OM3, Supplementation with Folate, vitamin B6 and B12 and/or Omega-3 fatty acids; tHcy, total homocysteine; VISP, Vitamin Intervention for Stroke Prevention; VITATOPS, Vitamins to Prevent Stroke; WAFACS, Women's Antioxidant and Folic Acid Cardiovascular Study.