Fig. 3.
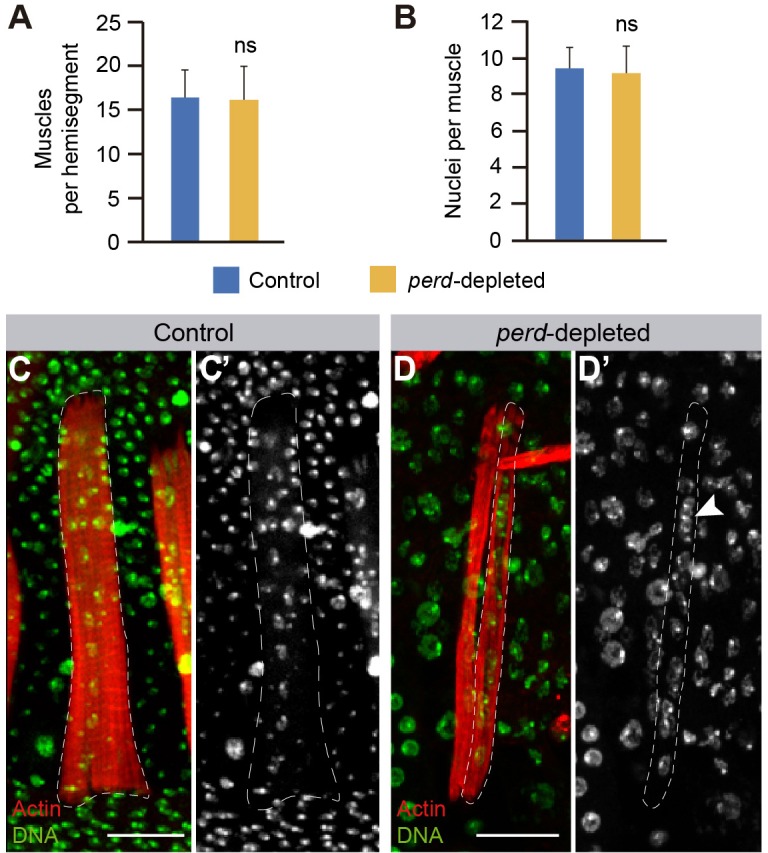
Reduction of perd function does not affect muscle number or number of nuclei per muscle. Quantification of the number of muscles per hemisegment (means±s.d., n = 9) (A) and nuclei per muscle (means±s.d., n = 9) (B) in wild-type and perd-depleted abdomens. ns, not significant. (C,D) Maximum intensity projection of muscles labeled with Rhodamine–Phalloidin (red) and the nuclear marker TO-PRO 3 (green). Non-muscle nuclei are also labeled with TO-PRO 3 but are located outside the muscle lumen. (D) Two perd-depleted muscles are shown but only the delineated one is complete and shows all its nuclei. (C) In wild-type muscles, nuclei are evenly distributed along the muscle length. This distribution is affected in perd-depleted muscles (arrowhead in D′). Scale bars: 20 µm.
