Fig. 4.
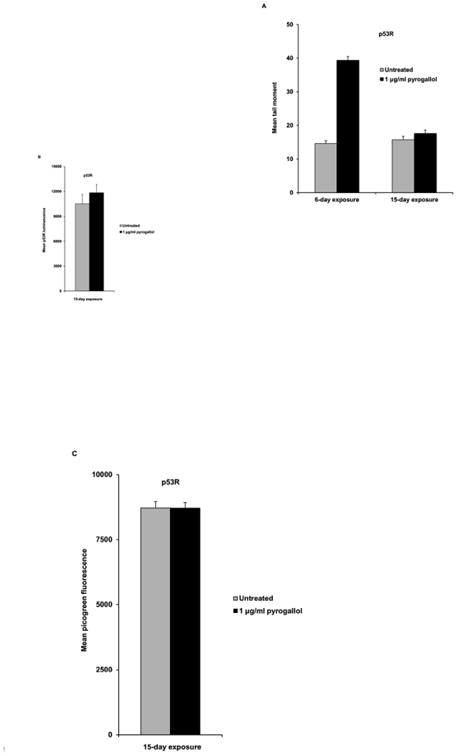
Chronic exposure to pyrogallol reduced the level of DNA damage in p53R cells. The neutral comet assay was performed on p53R cells, chronically exposed to pyrogallol at 1 μg/ml for 6 days or 15 days. Pyrogallol was added to the culture for the first time on day 0. The culture medium was replaced, and fresh pyrogallol was added on days 2 and 4 to cells exposed for 6 days. For cells treated for 15 days, the culture medium was replaced, and fresh pyrogallol was added on days 2, 4, 6, 8, and 13. At least 200 cells were analyzed per sample to calculate the mean tail moment of each cell population. The mean tail moment for each cell population the standard error of the mean reflecting between-cell variation in the same experiment are shown in (A). p53 reporter activity of cell populations chronically exposed to pyrogallol for 15 days was measured in a luciferase assay (B). The picogreen assay was performed at the same time to exclude the possibility that p53 reporter activity in chronically exposed cells was masked by elevated cytotoxicity (C).
