Figure 9.
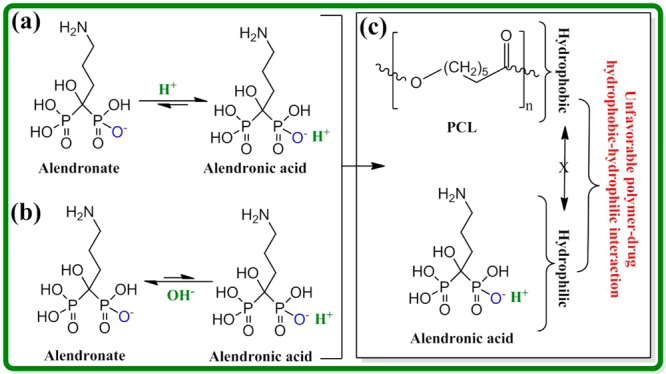
Schematic representation of the rate limiting steps for AD (salt or acid form) release. AD is liberated from the TCP surface in the presence of acidic (a) or basic (b) release medium, which is caused by the rate limiting TCP dissolution and/or equilibrium driven shift. In presence of PCL coating, final AD release is caused by the diffusion of AD from PCL coating through the unfavorable interaction between AD and PCL (non-rate limiting step) (c). In absence of PCL coating, AD release is governed by the rate limiting steps.
