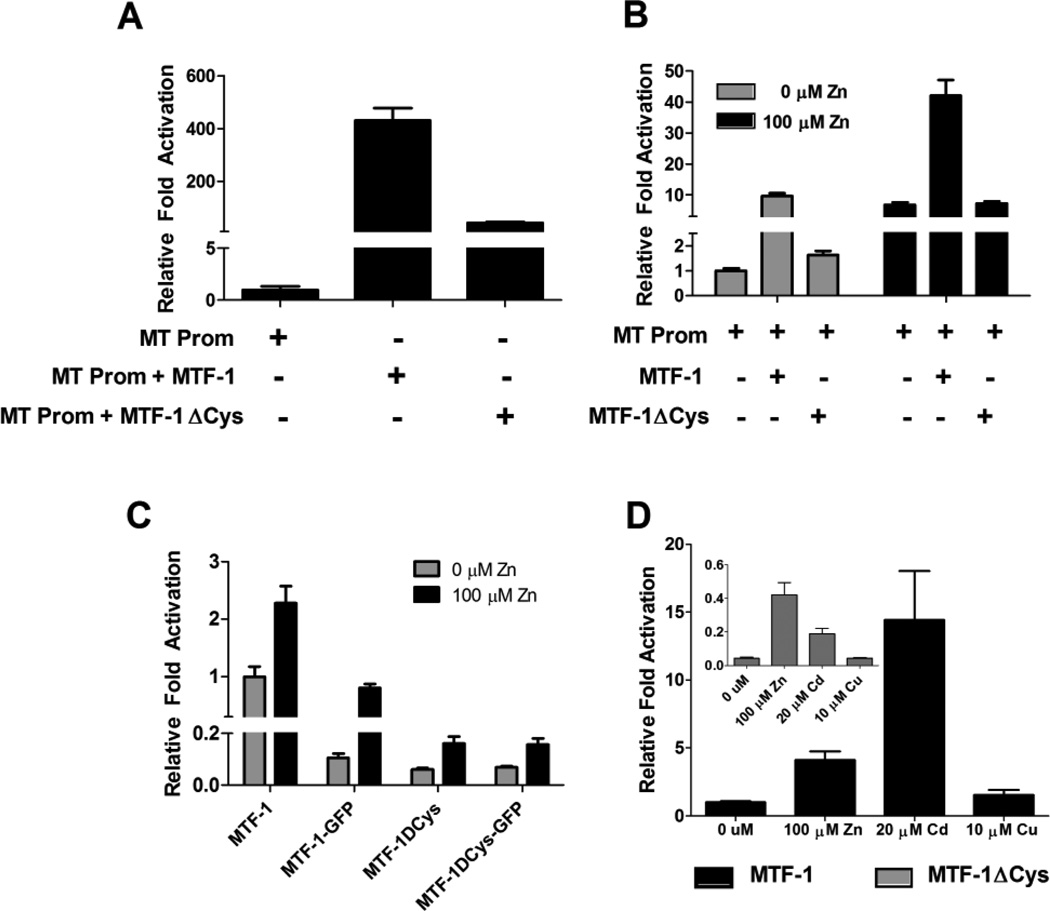
Figure 4.
Comparison of transactivation potential of MTF-1 versus MTF-1ΔCys. A) In transient transfection assays using MEF MTF-1 null cells, MTF-1 resulted in an order of magnitude greater induction of transcriptional activation of the zfMT-Luc promoter construct compared to MTF-1ΔCys. B) In transient transfection assays using Hepa1c1c7 cells, both MTF-1 and MTF-1ΔCys significantly enhanced basal activation of the zfMT-Luc promoter construct compared to endogenous MTF-1 alone. MTF-1 significantly increased the induction of luciferase activity in response to Zn treatment. There was no difference between endogenous MTF-1 activity and transfected MTF-1ΔCys in response to additional Zn treatment. C) A comparison of the transactivation of the zfMT-Luc promoter construct by all four MTF-1 constructs in response to Zn treatment in MEF MTF-1 null cells. MTF-1 transfection resulted on an order of magnitude greater activation of the zfMT-Luc promoter construct compared to the other three constructs. D) A comparison of the transactivation of the zfMT-Luc promoter construct by either MTF-1 or MTF-1ΔCys in response different metal treatments. A-D) Amount of each construct transfected per well: 20 ng of zfMT-Luc, 3 ng of Renilla vector, 23 ng of MTF-1 (3×109 copies), 21.8 g of MTF-1ΔCys (3×109 copies), 20.9 ng of MTF-1-GFP (3×109 copies) and 19.7 ng of MTF-1ΔCys-GFP (3×109 copies). Error bars represent one standard deviation: n = 6 replicates. The results shown in each panel are representative of two independent experiments.