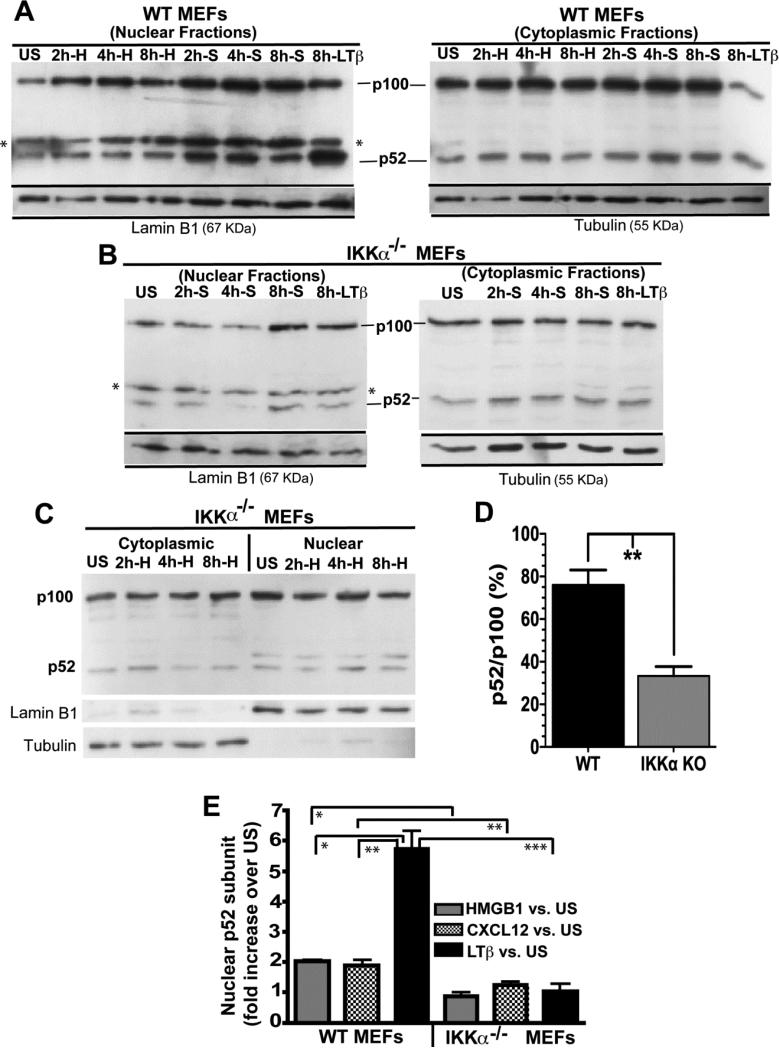
Figure 5. CXCL12 is a modest, IKKα-dependent inducer of NF-kB p52 nuclear translocation.
(A) Immortalized WT or (B and C) IKKα−/− MEFs were stimulated with either 50 ng/ml CXCL12, 100 ng/ml HMGB1 or 10 μg/ml of an antagonistic anti-LTβR antibody for the indicated times. S refers to CXCL12/SDF-1 and H denotes HMGB1. Nuclear and cytoplasmic protein fractions were analyzed by western blotting as shown with p100 and p52 identified by an anti-p100/p52 antibody. The asterisk in the immunoblot denotes a cross-reactive artifact band in the anti-p52 nuclear extracts. Immunoblots were stripped and re-probed with antibodies against Lamin B1 or β-Tubulin as protein loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic cell fractions, respectively. (D) Comparative analysis of p52:p100 levels in un-stimulated WT vs. unstimulated IKKα KO MEFs from 3 independent experiments (one of which is shown in panels A-C). E) Densitometric quantification of p52 nuclear import in WT and IKKα−/− cells in response to HMGB1, CXCL12/SDF-1 or LTβR stimulations at the 8 hr time point. Numbers represent 3 independent experiments. p52 signals were all normalized to lamin B1 as a nuclear protein reference control. Error bars are standard error of the mean. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 by two-tailed Student's t tests.