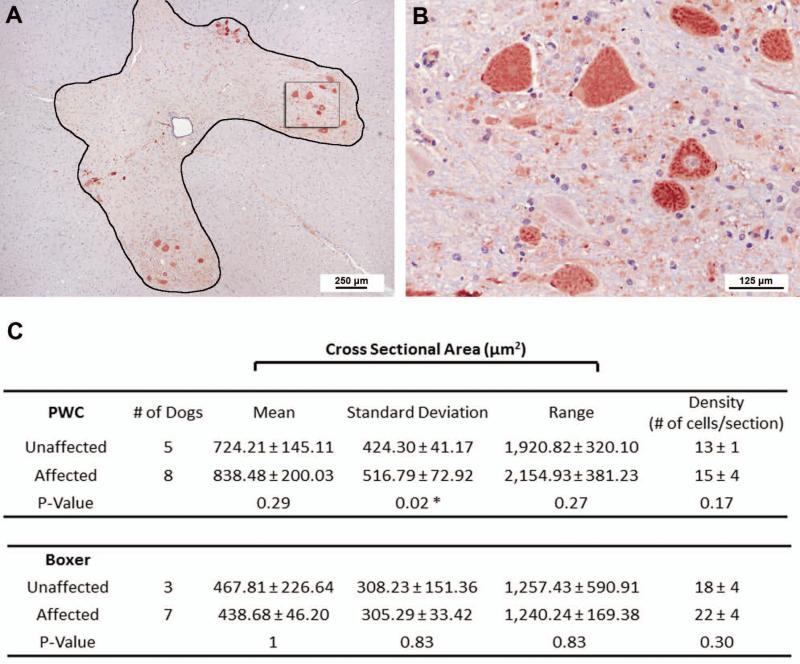
Figure 2.
Thoracic motor neuron morphometric measurements. (A, B) T7 spinal cord section from an unaffected 9 year old Boxer stained with ChAT. (B). Higher magnification of highlighted box within Rexed lamina 9 in A. This image is a representation of the normal motor neuron morphology seen in unaffected and affected dogs of both breeds. (C) Morphometric measurements obtained from PWC (top) and Boxers (Bottom). Pooled data indicate no difference in the motor neuron density between unaffected and affected samples of either breed (Affected boxers: one grade 1, three grade 2, one grade 3, and two grade 4 dogs; Affected PWC: two grade 2, two grade 3, and four grade 4 dogs). Likewise no differences were seen in the mean soma cross sectional area (CSA) or size range. In PWC's a significant difference was seen in the CSA standard deviation, suggesting more variability in soma area in affected dogs (p=0.02). One Way ANOVA indicated the difference in standard deviation is attributed to a significant difference between unaffected and late stage (grade 3-4) PWC samples (p= 0.04).