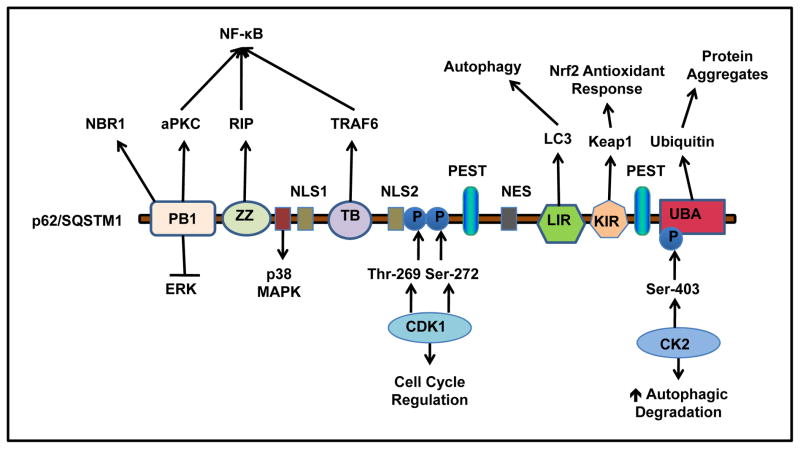
Figure 1. p62 structure, binding partners and functions.
p62 has Six distinct functional domains: PB1, ZZ, TB, LIR, KIR and UBA. PB1 domain self- and hetero- oligomerizes with other PB1 containing proteins, such as NBR1, ERK and aPKC. p62 binds with RIP at ZZ zinc finger region, and TRAF6 at TB domain, which regulates NF-κB activation. At residues 173–182, p62 interacts with p38 MAPK. p62 interacts with LC3 through the LIR, and keap1 through the KIR. The c-terminal UBA domain of p62 binds to ubiquitin. p62 has two PEST sequences that are targets for post translation modifications and degradation. p62 is phosphorylated by CDK1 at T269 and S272 that regulates cell cycle. p62 is phosphorylated by CK2 at S403 that enhances autophagic degradation of ubiquitinated proteins. p62 also contains two NLS sequences and a NES sequence which allow p62 shuttling into and out of nucleus.