Fig. 5.
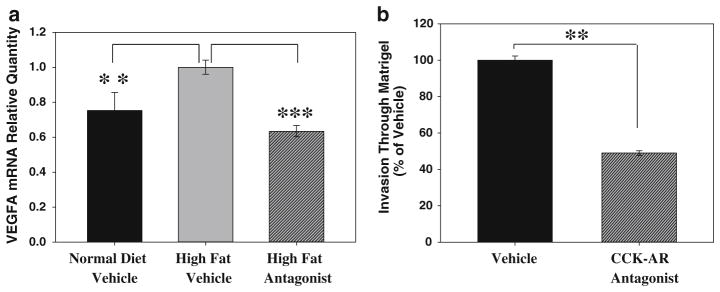
CCK-AR antagonist treatment alters VEGF-A expression in vivo and decreases tumor cell invasiveness in vitro. a Panc-02 tumors from mice on the high-fat diet (gray bar) had increased expression of VEGF-A mRNA when compared to tumors from mice fed normal chow (black bar)(**p < 0.0002). This increase in VEGF-A expression was reversed with the CCK-AR antagonist treatment (hatched bar, ***p < 6 × 10−9). Tumors from 5 to 6 mice were analyzed for each treatment group. b Vehicle-treated Panc-02 cells (black bar) clearly moved through a Matrigel-coated filter in vitro. However, in the presence of the antagonist (100 nM, hatched bar), the number of invasive Panc-02 cells moving through Matrigel was reduced by more than 50 % (**p = 1.33 × 10−6). Error bars denote the standard error of the mean of the individual assays normalized to vehicle treatments
