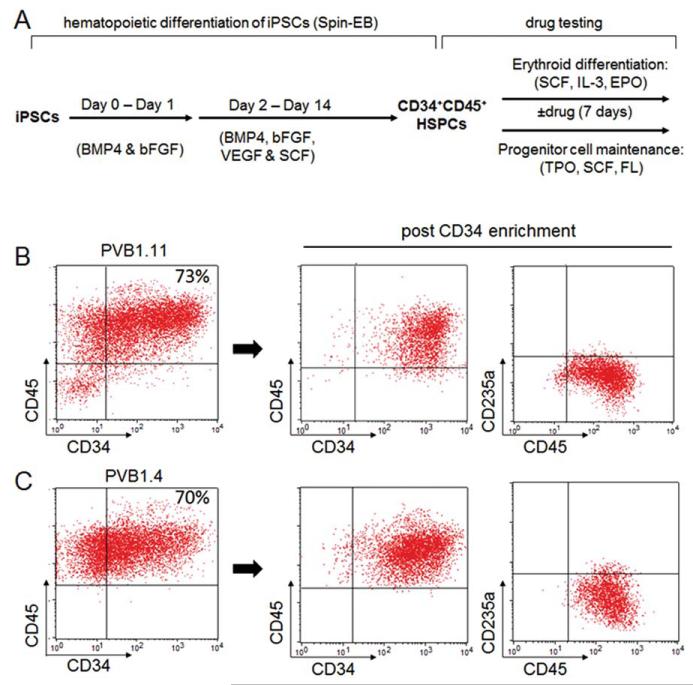
Figure 2.
The in vitro hematopoietic differentiation-based disease modeling and drug testing. (A): A diagram of the spin-EB hematopoietic differentiation procedure and the following drug testing experiments using the iPSC-derived hematopoietic progenitors. iPSCs from both PV patients and controls were first differentiated into CD34+CD45+ hematopoietic progenitors using serum-free medium in the presence of bFGF, BMP4, VEGF, and SCF. The differentiated hematopoietic progenitors were then used to assess their responses to JAK inhibitors in both erythroid differentiation and progenitor self-renewal assays. (B): Flow cytometry analysis of the suspension cells harvested at the end of the 14-day spin-EB differentiation of PVB1.11 (JAK2 wild-type iPSC from a PV patient) showed high percentage of CD34+CD45+ cells. The CD34+CD45+ hematopoietic progenitor cells can be further enriched by CD34 positive selection. (C): Compared to PVB1.11, the JAK2 V617F-positive iPSC PVB1.4 (derived from the same patient as PVB1.11) showed comparable level of CD34+CD45+ hematopoietic cells at the end of the 14-day spin-EB differentiation. Abbreviations: BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; EPO, erythropoietin; FL, Flt-3 ligand; HSPCs, hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells; IL-3, interleukin 3; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells; SCF, stem cell factor; TPO, thrombopoietin; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.