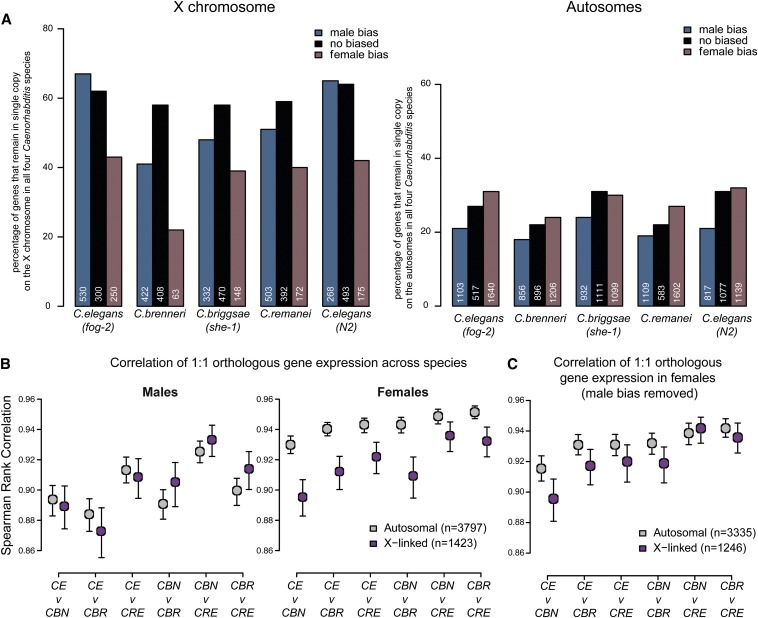
Figure 6.
Conservation of orthologous gene expression across species. (A) On the X, male-biased genes are more likely to be conserved than female-biased genes. For each species, genes were divided into three categories: male-biased (blue), female-biased (purple), and nonbiased (black). Within each category, we identified 1:1:1:1 Caenorhabditis orthologs that are located on the same chromosome (X, left) or autosome (right) in all four species. X-linked genes have a higher tendency than autosomal genes to remain on the same chromosome and in single copy. Similarly, X-linked male-biased genes show greater tendency to remain in single copy compared to X-linked female-biased genes. (B) Correlation of 1:1 orthologous gene expression between Caenorhabditis indicates that X-linked expression is evolving faster in females. Between any two species, Spearman rank correlation of 1:1 orthologous gene expression was plotted for males (left) and females (right). As determined by bootstrapping, 95% confidence intervals are indicated. (CE, C. elegans; CBN, C. brenneri; CBR, C. briggsae; CRE, C. remanei). (C) High male-biased genes are removed from correlation analysis shown in B, right.