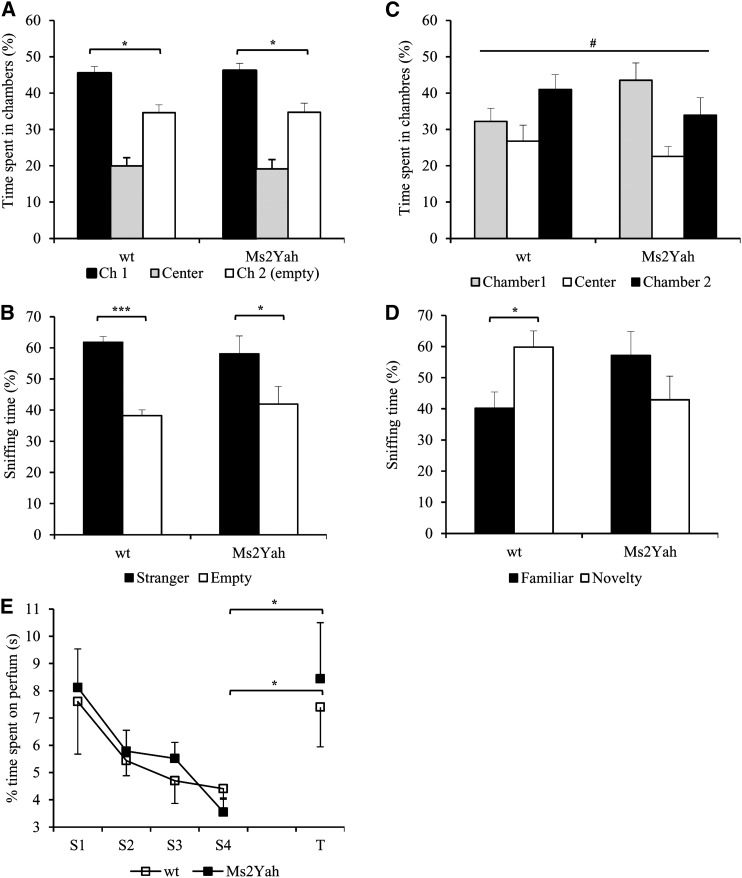
Figure 3.
Social novelty performance is altered in the Ms2Yah mice. (A–D) Percentage of time spent in the different chambers (A and C) and of time spent sniffing the cages (B and D). In A and B, chamber 1 contained a mouse (familiar) and chamber 2 is empty. The WT mice showed a strong preference for the chambers and the cage containing an unfamiliar mouse while monosomic mice showed no significant interaction with the congener. In C and D, a new mouse (novel) was placed in chamber 2. Here the WT mice had a preference for the chambers or spent more time sniffing the cage with the novel individual whereas the Ms2Yah mice failed to interact with the new mouse and spent more time in the chamber with the familiar individual. In E, odor learning and discrimination were controlled to exclude the olfactory defect in the Ms2Yah mice. Data shown are mean + SEM for each strain. Statistical analyses are based on Student’s t-test (***P < 0.001; **P > 0.01; *P > 0.05); # n.s. Chamber1 versus Chamber2.