Figure 2. Vibrio cholerae infection of zebrafish using brine shrimp as a vehicle.
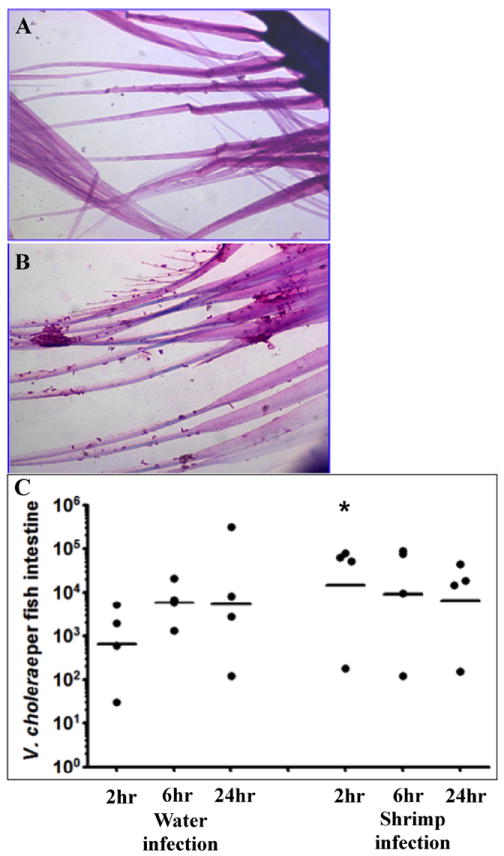
Brine shrimp cultures are produced using brine shrimp eggs (Artemia cysts) and a brine shrimp hatchery (Aquatic Eco-systems). Freshly hatched brine shrimp (< 24 hours post hatch) were removed from the hatchery and washed 3X in tap water to remove excess salt. One hundred microliters of washed brine shrimp were added to 1 ml of 108 cfu of V. cholerae and mixed gently on a rotator for 15 minutes at room temperature. A). Hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) stained brine shrimp without V. cholerae. B). H & E stained brine shrimp after incubation with V. cholerae. C). Time course of colonization for fish infected after water exposure or using brine shrimp as a vehicle. Each dot represents the data from one fish and the horizontal bar indicates the mean bacterial load per fish. Total colonization per intestine was calculated after plating serial dilutions of intestinal homogenate 24 hr post infection. * p < 0.05.
