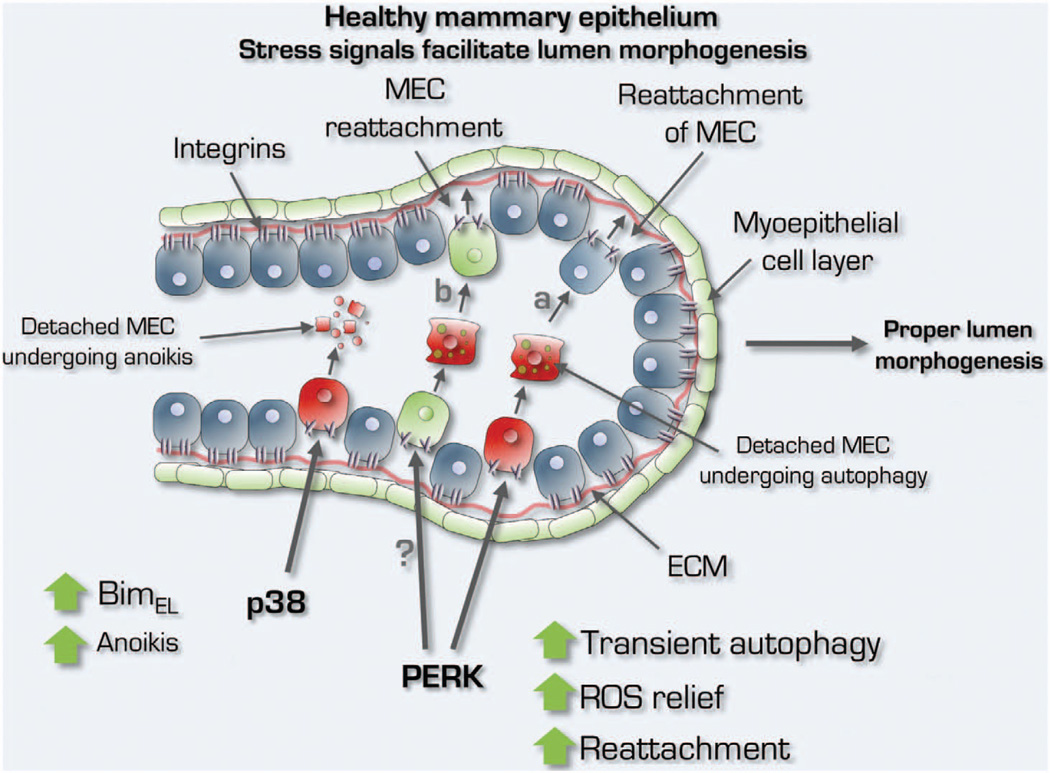
Figure 1.
The role of p38 and PERK signaling in normal mammary gland biology. Physiological activation of p38 and PERK signaling by cell detachment governs mammary epithelial cell (MEC) lumen integrity that is lost during cancer initiation. In healthy MGs, whereas lumen formation is favored by p38SAPK- and BimEL-mediated apoptosis, PERK activation is required for cell survival to allow transient movement of MECs (a) within the luminal layer and/or hypothetically for the protection of progenitors and stem cells (b) that detach from the ECM within a plastic epithelium during ductal/acinar morphogenesis. The protective function of PERK is via a timed and tightly regulated ‘survival license’ during which autophagy and antioxidant gene induction protect ECM-detached cells from anoikis.