Figure 3.
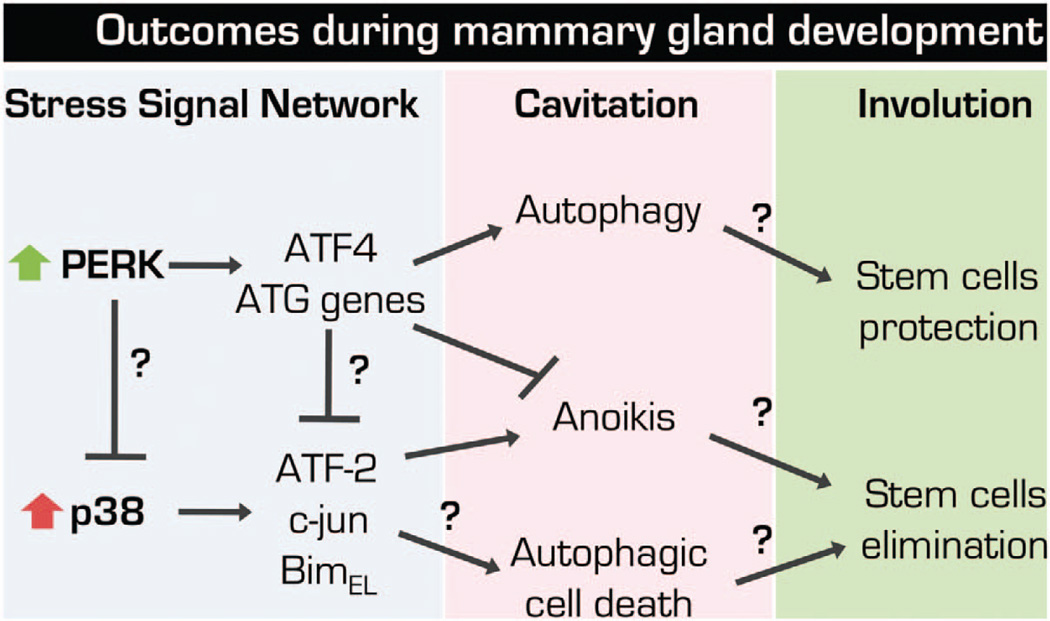
Hypothetical implications and open questions on the crosstalk between p38SAPK and PERK pathways during MG morphogenesis. p38SAPK and PERK are activated simultaneously after ECM-detachment; however, how can such opposing activities (PERK pro-survival and p38SAPK pro-apoptotic) be reconciled in the comprehensive setup of the mammary gland epithelium is largely unknown. It is possible that PERK signaling directly inhibit p38SAPK activity via post-translational modifications, through the translational repression of p38SAPK-dependent anoikis executors (that is, BimEL) or via upregulation of ATF4. However, these signals are integrated during the survival and anoikis stages of cell fate may markedly influence during hollow lumen morphogenesis. Finally, this network may have a critical role during MG development cycle. We hypothesize that PERK-dependent arm could protect the stem cell compartment during MG involution, whereas p38 signaling could compensate to maintain a homeostatic number of these cells and progenitors that if in excess could result in an exacerbated proliferation in the expansion phase. Thus, both pathways may be critical to maintain the homeostasis of the stem and progenitor cell compartments and proper MG morphogenesis. ATG genes, autophagy genes.