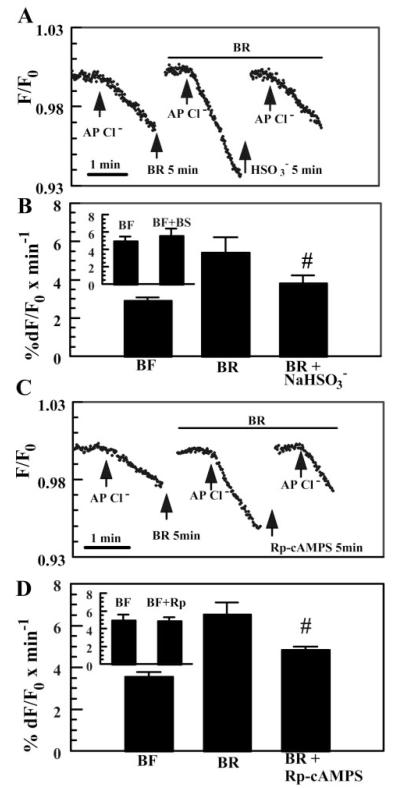
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of sAC and PKA reduces -activated apical Cl− permeability. A: effect of the weak sAC agonist (20 mM) on apical Cl− permeability. Bisulfite solutions were prepared by adding 20 mM NaHSO3 directly to Cl−-free and -rich solutions. Equimolar Na-gluconate was added to all other solutions. Osmolality was within ±5 mosmol/kgH2O for all solutions. Breaks in the trace indicate periods of Cl−-free wash (at least 5 min). B: summary data for A. #Significantly different from BR (n = 5, P < 0.05). Inset: independent experiments comparing apical Cl− permeability in -free Ringer solution (BF) with or without (BS). C: inhibition of -activated apical Cl− permeability by the PKA inhibitor Rp-adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphorothioate (Rp-cAMP[S]; 50 μM). D: summary data for C. #Different from BR (n = 5, P < 0.05). Inset: independent experiments comparing apical Cl− permeability in -free Ringer solution with or without Rp-cAMP[S].