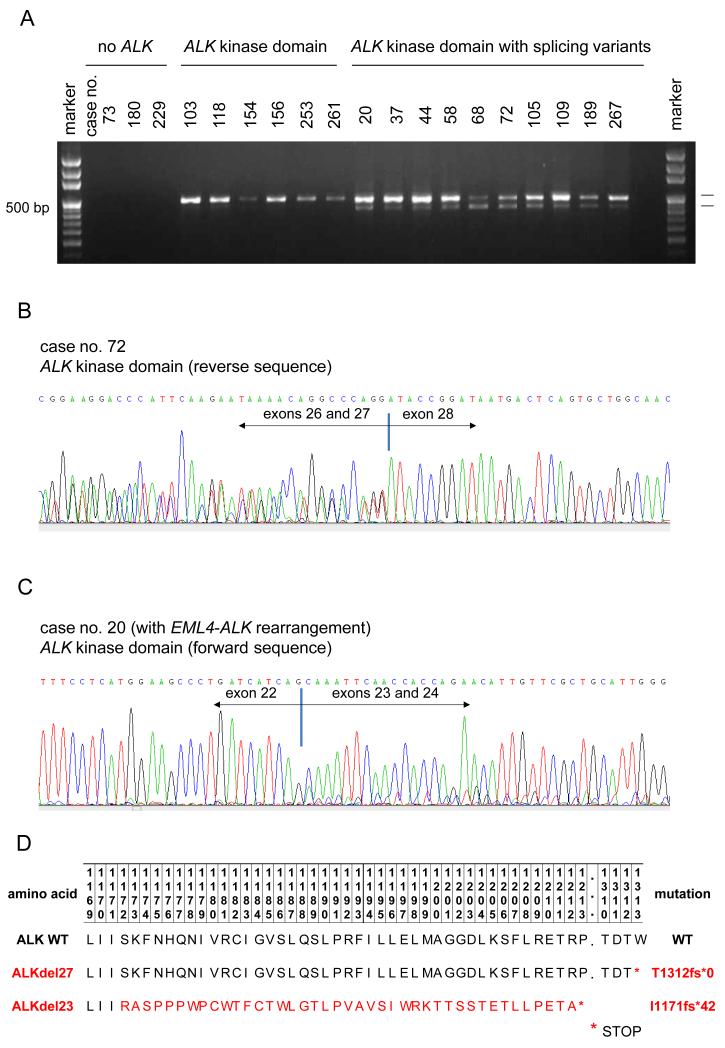
FIGURE 1.
Screening for ALK kinase domain splicing variants in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
A. Reverse transcriptase PCR using primers that flank exons 20 to 29 of ALK (encompass the kinase domain). Cases with or without ALK kinase domain expression, and those expressing ALK slicing variants;
B. Sequence chromatogram of a tumor specimen with complete skipping of exon 27 of ALK (ALKdel27). Representative sequences from cDNA isolated from case no. 72 highlighting the ALK exon 26-exon 27 and ALK exon 26-exon 28 co-existing sequences;
C. Sequence chromatogram of a tumor specimen with complete skipping of exon 23 of ALK (ALKdel23). Representative sequences from cDNA isolated from case no. 20 highlighting the ALK exon 22-exon 23 and ALK exon 22-exon 24 co-existing sequences. Reference ALK gene sequence (NM_004304.3; homo sapiens ALK mRNA);
D. Proposed amino acid sequence of wild type (WT) ALK, ALKdel27 and ALKdel23. The latter truncated proteins generate early stop codons. *denotes a STOP codon sequence.