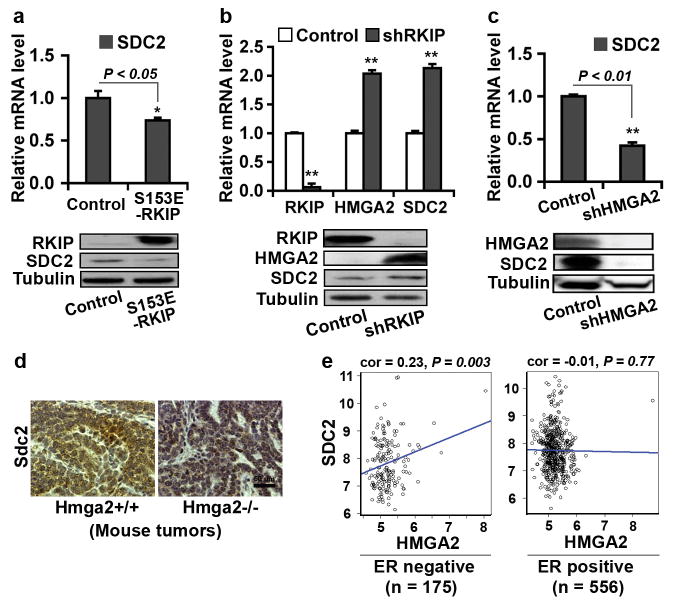
Figure 4.
Expression of RKIP or depletion of HMGA2 inhibits SDC2 expression. (a) RKIP inhibited SDC2 expression. 1833 cells were stably transduced with S153E-RKIP or vector control. Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR for SDC2 mRNA (upper panel) or by immunoblotting for RKIP and SDC2 protein (lower panel). (b) Depletion of RKIP by RKIP shRNA induced HMGA2 and SDC2 expression. MDA-MB-435 cells were stably transduced with RKIP shRNA (shRKIP) or scrambled shRNA (Control). Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR (upper panel) and immunoblotting (lower panel) for RKIP, HMGA2 and SDC2 expression. (c) Depletion of HMGA2 by HMGA2 shRNA inhibited SDC2 expression. 1833 cells were stably transduced with HMGA2 shRNA (shHMGA2) or scrambled shRNA (Control). Samples were analyzed by qRT-PCR (upper panel) and immunoblotting (lower panel) for HMGA2 and SDC2 expression. (d) Loss of Hmga2 in MMTV-Wnt1 transgenic mouse breast tumors inhibited SDC2 expression. Mouse primary breast tumors were obtained from MMTV-Wnt1/Hmga2+/+ or MMTV-Wnt1/Hmga2-/- mice. Murine Sdc2 protein was analyzed by immunostaining. (e) Significant positive correlation between HMGA2 and SDC2 expression observed in ER-negative (n = 175) (Left) but not in ER-positive (n = 556) (Right) breast cancer patient data (Br731). Correlations were determined by Pearson's correlation coefficient. P, Student t test. (a-c) GAPDH was used as the normalization control for mRNA; Tubulin was used as a loading control for protein. Data are mean ± s.e., n = 3. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.