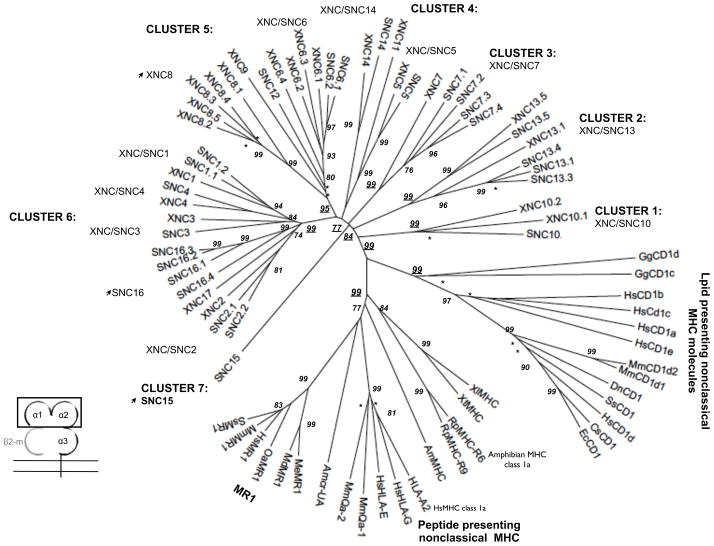
Fig 2. The phylogenetic relationships of XNC and SNC α1/α2 domains compared to selected vertebrate classical and nonclassical MHC genes.
The neighbor-joining tree was constructed from amino acid alignments of the alpha 1 and alpha 2 domains using pairwise gap deletions and the p-distance method to estimate evolutionary distance. The tree was drawn using MEGA 5.2. and confidence values were measured using 10,000 bootstrap replications with the values indicated at key nodes and * indicating values < 50. Arrows indicate non-classical subfamilies within the Xenopodinae without clear orthologous relationships between X. laevis and X.tropicalis. Species abbreviations are: Xl, X. laevis, Xt, X. tropicalis; Hs, human; Mm, mouse; Ss, pig; Gg, chicken; Me, Tammar wallaby; Wd, short-tailed opossum, Oa, sheep; Ec, horse; Cs, rhinoceros; Dn, nine-banded armadillo; Rp, northern leopard frog and Amcr, Galapagos marine iguana.