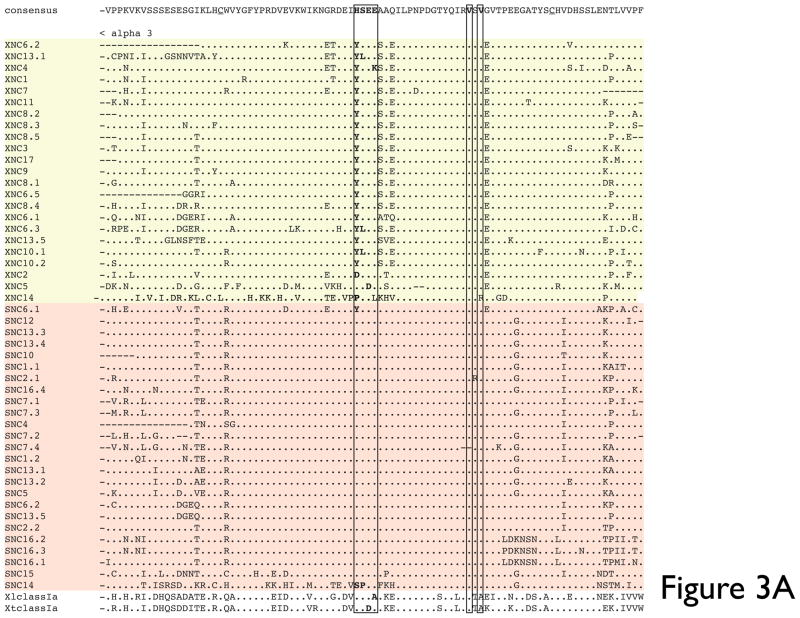
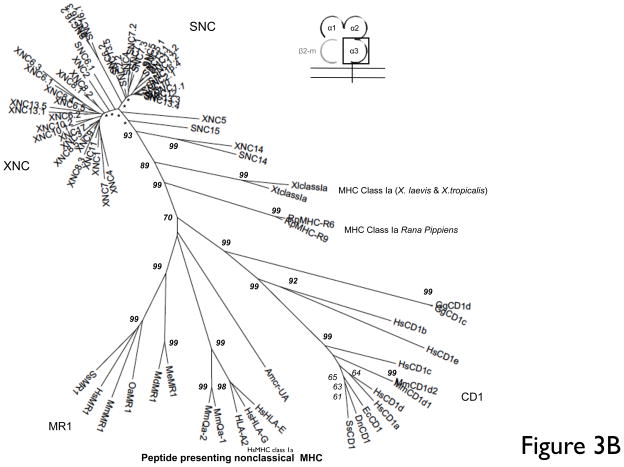
Fig 3. Multiple deduced amino acid sequence alignment and phylogenetic relationships of the α3 domains of X. tropicalis and X. laevis nonclassical MHC genes (SNC and XNC).
(A) Deduced amino acid alignment of XNC and SNC α3 domains with X. laevis and X. tropicalis MHC class Ia. A consensus sequence is shown at the top and dots indicate amino acids identical to this sequence; (-) represent gaps in the alignment and conserved cysteines are in bold and underlined. The MHC class I CD8 binding site is boxed and indicated in bold. (B) The neighbor-joining tree was constructed from amino acid alignments of the alpha 3 domains using pairwise gap deletions and the p-distance method to estimate evolutionary distance. The tree was drawn using MEGA 5.2. and confidence values were measured using 10,000 bootstrap replications with the values indicated at key nodes with * indicating values <50. Species abbreviations are: Xl, X. laevis, St, S. tropicalis; Hs, human; Mm, mouse; Ss, pig; Gg, chicken; Me, tammar wallaby; Wd, short-tailed opossum, Oa, sheep; Ec, horse; Cs, rhinoceros; Dn, nine-banded armadillo; Rp,northern leopard frog and Amcr, Galapagos marine iguana.