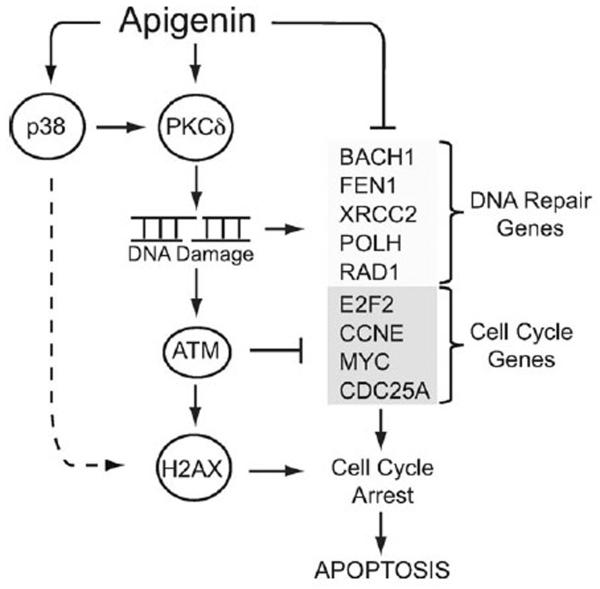
Fig. 6.
Working model of apigenin-induced DNA damage. Apigenin induces DSBs, ATM and H2AX phosphorylation in a PKCδ-dependent pathway, while p38 modulates apigenin-induced DNA damage independent of ATM. Apigenin-induced down-regulation of cell cycle control genes and ATM activation led to cell cycle arrest at the G1/S transition. Down-modulation of genes involved in DNA repair by apigenin indicates that cells may be unable to repair apigenin-induced DNA damage, hence triggering apoptosis.