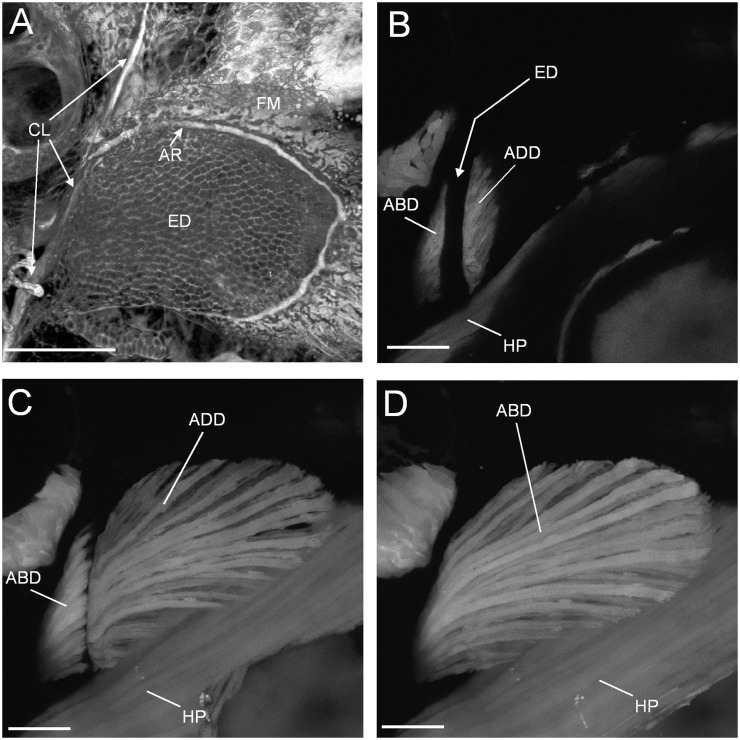
Fig. 1.
Confocal images of the endoskeletal disc and pectoral fin musculature in 5 dpf larval zebrafish. Lateral view confocal slices (B–D) from the same 3D stack. (A) The endoskeletal disc (ED), distal fin membrane (FM), and basal cleithrum (stained in vivo with calcein green). AR is the pectoral fin artery that delimits the endoskeletal disc. (B) Abductor (ABD) and adductor (ADD) musculature in cross-section near their proximal end. The endoskeletal disc that separates would be in the space indicated. Hypaxial musculature (HP) lies medially to the fin. (C) Adductor muscle and a section through the abductor muscles. (D) Extent of the abductor in lateralmost view. Scale bars = 100 μm. Reprinted with permission from Thorsen and Hale (2005).