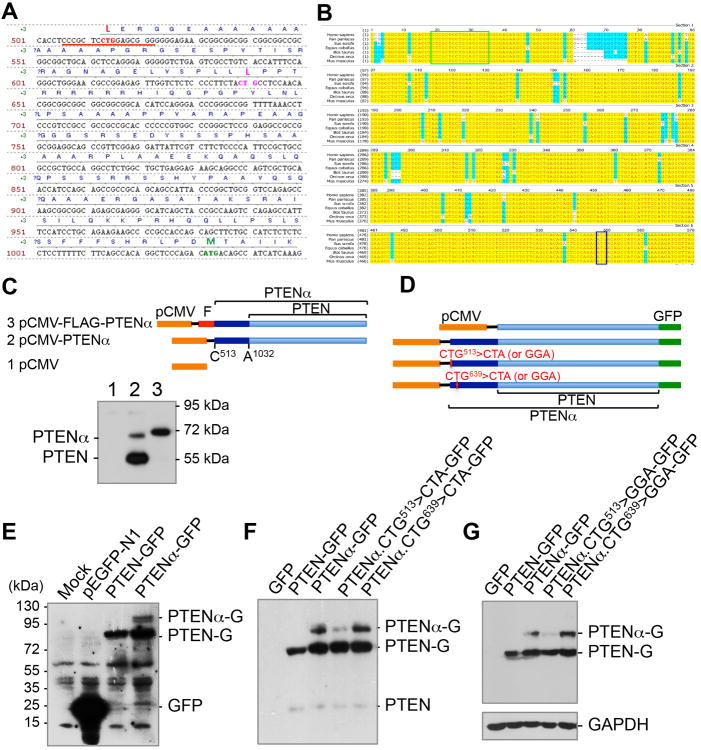
Figure 1. Identification and validation of PTENα.
(A) Sequence of the 5′-UTR region of Homo sapiens PTEN mRNA. Two potential CUG sites (red and pink) as well as the normal ATG start site (green) are highlighted.
(B) The 5′-UTR of PTEN containing the 16-bp CUG-centered palindromic motif is evolutionary conserved. Phylogenetic analysis of the 5′-UTR of PTEN mRNA in bonobo (Pan paniscus), wild boar (Sus scrofa), horse (Equus caballus), cattle (Bos taurus), killer whale (Orcinus orca) and mouse (Mus musculus). The 16-bp palindromic sequence is highlighted in a green box and the ATG start codon of canonical PTEN is in a blue box.
(C) PTEN cds with a CUG513-starting 5′-UTR region (PTENα) was constructed under a CMV promoter and expressed with and without a N-terminal FLAG tag. Human HEK293T cells were transfected with indicated expression plasmids, followed by Western blotting analysis using a PTEN monoclonal antibody against its C-terminal region.
(D) A different set of constructs of PTEN and PTENα with a C-terminal GFP tag, in which one of the two possible CTG sites (CTG513 or CTG639) was mutated to CTA or GGA.
(E-G) Mutation of CTG513 but not CTG639 eliminates the expression of PTENα. C-terminal GFP-tagged PTENα expression plasmids with and without CTG513>CTA or CTG513>GGA mutation(s) were introduced in human HCT116 colon cancer cells, followed by detection of GFP-PTENα variants. E, The expression of GFP-tagged PTEN or PTENα was confirmed by Western blotting using a GFP antibody. F and G, mutation of CTG513 but not CTG639 into CTA or GGA results in the disappearance of PTENα. PTENα-G and PTEN-G, PTENα or PTEN with a C-terminal GFP tag.
See also Figure S1.