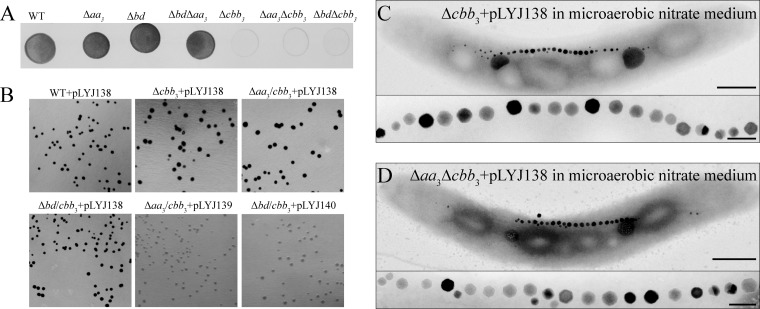
FIG 4.
(A) Nadi assay of the WT and various mutant strains. This method is commonly used to specifically detect cytochrome c oxidase activity (26), which is based on the rapid formation of indophenol blue from colorless α-naphthol catalyzed by cytochrome c oxidases with N,N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine monohydrochloride as an exogenous electron donor. Five microliters of cultures grown anaerobically for 24 h, which were adjusted to about 107 CFU/ml, were dropped onto an agar plate in the presence of nitrate. Strains were incubated at 30°C for 4 days under anaerobic conditions and photographed after a 5-min Nadi reaction. (B) Nadi assay of anaerobically grown complementation strains. Plasmid pLYJ138 contains a WT cbb3 allele, while pLYJ139 and pLYJ140 harbor WT aa3 and bd alleles, respectively. (C) TEM images of Δcbb3 and Δaa3 Δcbb3 strains complemented with plasmid pLY138, harboring the WT cbb3 allele, grown in microaerobic nitrate medium. Bars, 500 nm (whole cells) and 100 nm (magnetosomes).