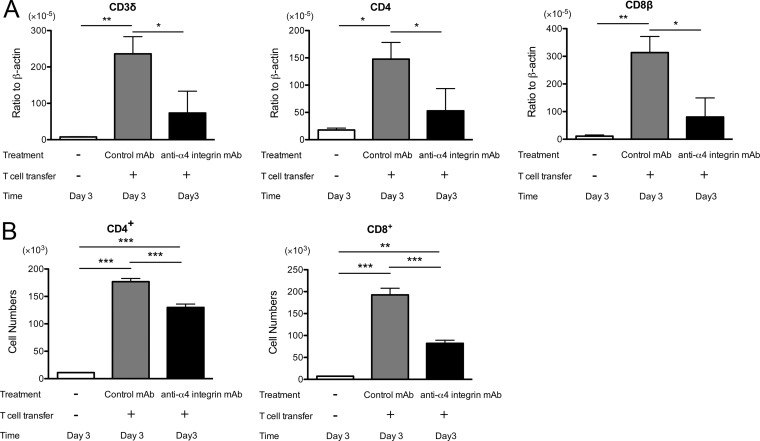
FIG 3.
mRNA levels for T cell markers (CD3δ, CD4, and CD8β) (A) and numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (B) are markedly lower during the early stage of reactivation of T. gondii infection in the brains of nude mice that received immune T cells with anti-α4 integrin MAb treatment than in those with the cell transfer with control MAb. Nude mice were infected with 10 cysts of the ME49 strain orally and treated with sulfadiazine for 3 weeks beginning 7 days after infection. Groups of animals received immune T cells (0.9 × 107 cells) pretreated with either anti-α4 integrin or a control MAb intravenously 4 weeks after infection. Thereafter, the mice received the MAb (200 or 250 μg) intraperitoneally every other day. Sulfadiazine treatment was discontinued 3 days after the cell transfer, and mRNA levels for the T cell markers and numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the brains were determined by real-time RT-PCR and flow cytometry 3 days after discontinuation of sulfadiazine treatment (see Materials and Methods). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. The error bars indicate standard errors.