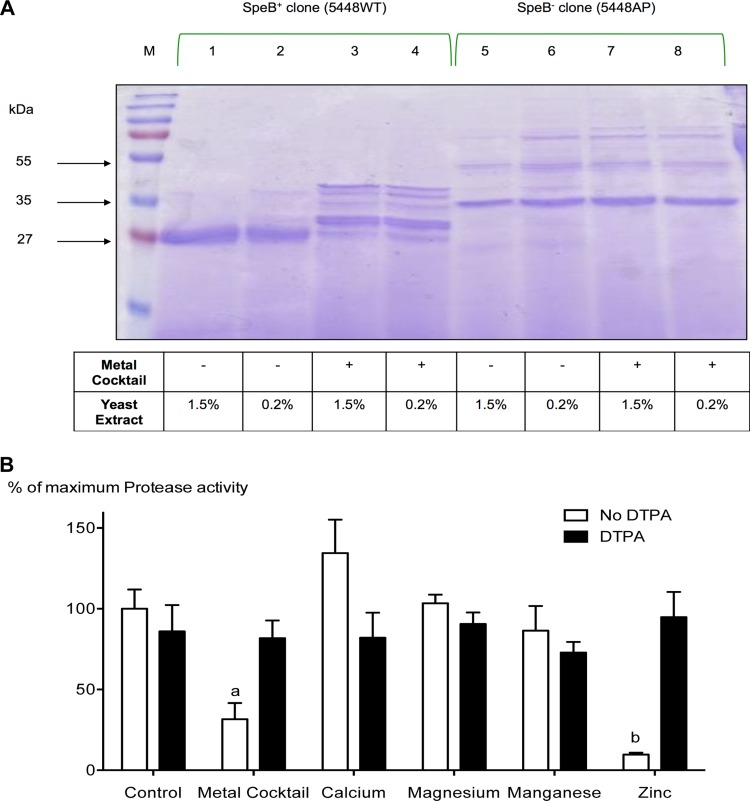
FIG 1.
Zinc inhibits SpeB maturation and its activity during growth, and chelating zinc reverses this inhibition. (A) GAS isolate 5448WT was grown in the presence or absence of 1 mM (final concentration) the metal cocktail CaCl2, MgCl2, MnCl2, and ZnSO4. The secreted proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized using Coomassie staining (lanes 1 to 4). Strain 5448AP, an isogenic mutant that lacks the ability to produce SpeB, was grown under the same conditions and used as a negative control (lanes 5 to 8). Since yeast extract contains appreciable amounts of transition metals (37), we grew both the SpeB-negative (5448AP) and SpeB-positive (5448WT) isolates at 0.2% (even-numbered lanes) or 1.5% (odd-numbered lanes). Irrespective of the yeast extract concentration, there was a notable difference in the secreted-protein profiles of strain 5448WT grown in control medium (lanes 1 and 2) versus medium containing metal supplements (lanes 3 and 4). Lanes 5 to 8, which contain the SpeB-negative control, showed no significant difference in their secreted-protein profiles. (B) GAS isolate 5448WT was grown in the presence of 1 mM individual metal (CaCl2, MgCl2, MnCl2, or ZnSO4) or a cocktail of the metals, with and without the addition of the metal chelator DTPA. After 18 h in culture, the culture supernatants were harvested, concentrated, and used to measure the cysteine protease activity of SpeB using an EnzChek assay, as described in Materials and Methods. The data presented are means and standard deviations (SD) (n = 4). The experiments were repeated four times in triplicate, and each data point represents the percentage of maximum protease activity at 1 mM the specified metal and/or DTPA. The data were normalized to the total protease activity obtained in the absence of metals or chelator (control group). Two-way ANOVA analyses revealed significant interaction (P < 0.001) between bacterial cultures containing different metal groups and their DTPA treatments. a and b indicate significant differences (P < 0.001) within treatments (with and without DTPA) and between cultures containing different metal groups and the specified group by Bonferroni post hoc analysis.