Figure 4.
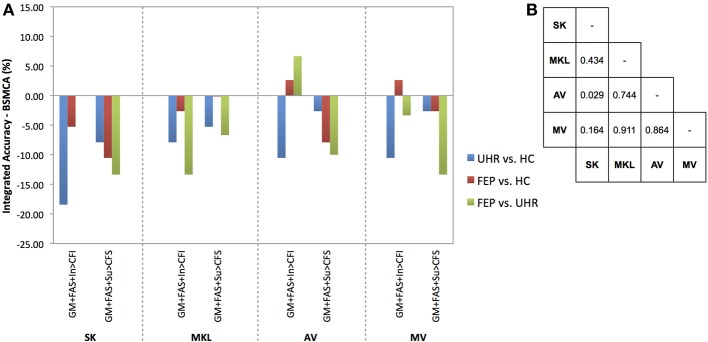
(A) Difference between the integrated accuracy achieved using SK, MKL, AV, or MV, and the BSMCA, discriminating UHR and FEP subjects from HCs, and each other, using three-way combinations of sMRI, DTI, and fMRI data. (B) Results of McNemar's tests comparing subject classifications achieved by each integrative method collapsed across SVM contrasts and data combinations. SK, Un-weighted simple sum of kernels; MKL, Multi-Kernel Learning; AV, Prediction Averaging; MV, Majority Voting; GM, grey matter; FAS, fractional anisotropy skeleton; In, generation of an overt verbal initiation response; Su, generation of an overt verbal suppression response; RI, repetition of “REST” during the initiation condition; RS, repetition of “REST” during the suppression condition; CFI, visual cross-fixation during the initiation condition; CFS, visual cross-fixation during the suppression condition.
