Figure 3.
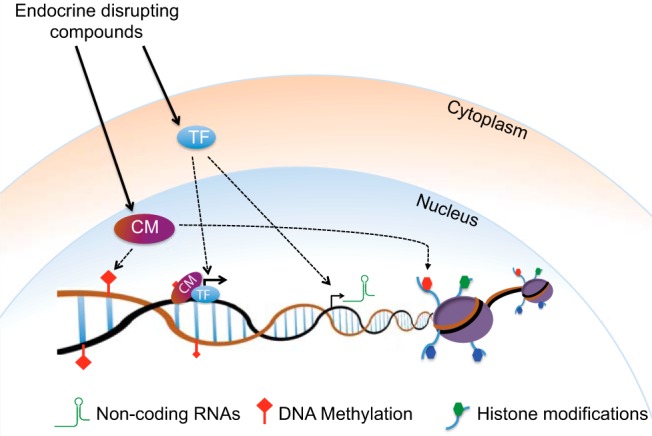
A general model depicting epigenetic alterations upon exposure to EDCs. EDCs bind to steroid receptors, and other TFs, thereby changing the local chromatin states and expression of various chromatin modifiers (CM) such as histone and DNA modifiers or ncRNAs. Moreover, EDCs can change the composition or the activity of epigenetic chromatin regulator complexes and thereby act directly on the global epigenome.
