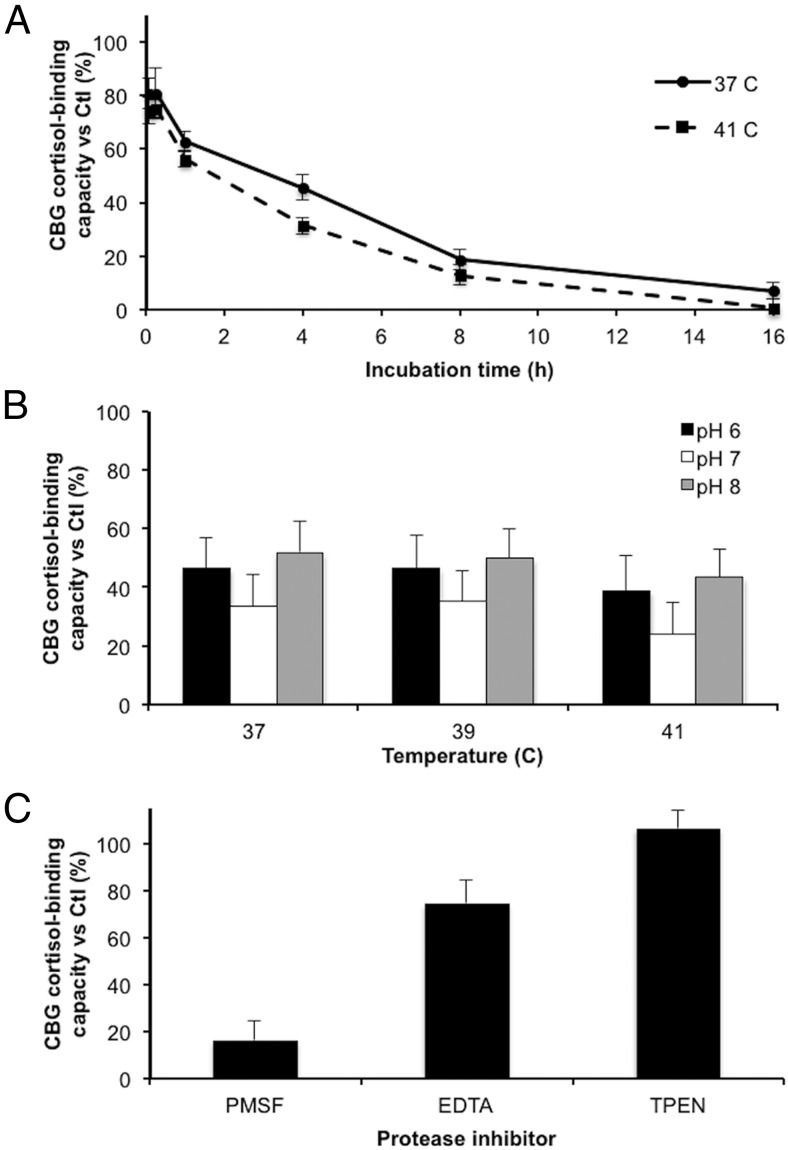
Figure 2.
Reduction in the cortisol-binding capacity of CBG in human serum after incubation with P. aeruginosa media is time-, temperature-, and pH-dependent, and requires the presence of zinc. A, The cortisol-binding capacity of CBG was measured after incubation of human serum with P. aeruginosa media for 5 minutes, 15 minutes, 1 hour, 4 hours, 8 hours, and 16 hours at 37°C or 41°C. Incubation at 41°C led to a greater decrease (P < .001) in activity than incubation at 37°C. B, Human serum was incubated with P. aeruginosa media for 8 hours at pH 6, 7, or 8, and at 37, 39, or 41°C. The cortisol-binding capacity of CBG was lower after incubations at pH 7 than at pH 6 and 8 for all temperatures tested (P = .0065). C, Human serum was incubated with P. aeruginosa media in the presence of 1 mM PMSF (serine/cysteine protease inhibitor), 5 mM EDTA (divalent cation inhibitor), or 20 ng/μl TPEN (specific zinc chelator) for 16 hours at 37°C. All incubations were performed in triplicates and data are presented as mean percentage ± SD of steroid-binding activity relative to a control.