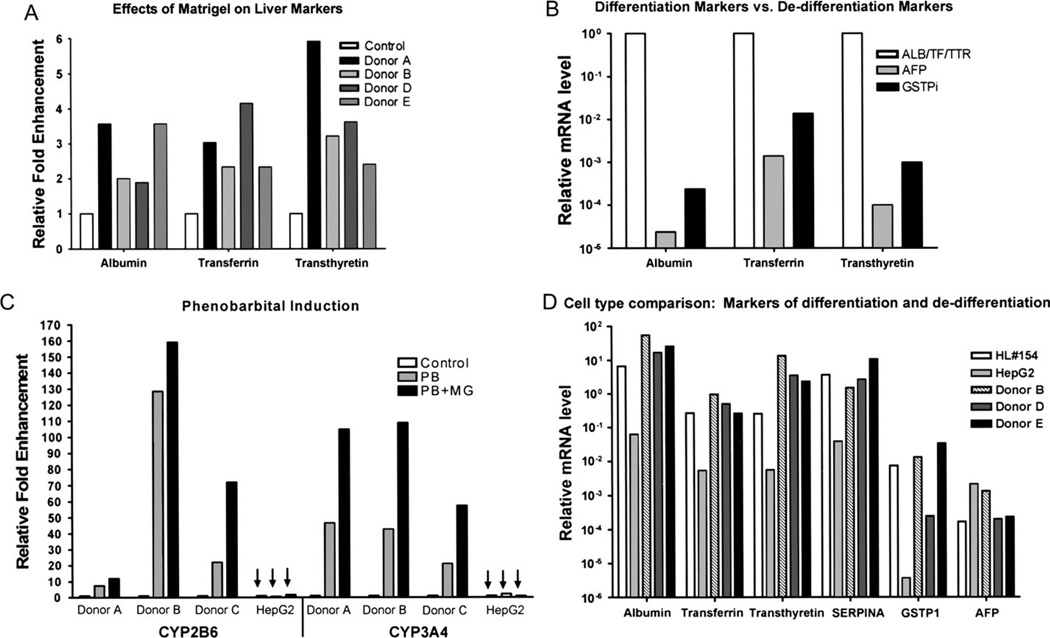
FIG. 3.
Effects of Matrigel addition on differentiation status of primary human hepatocyte cultures. Total RNA was isolated from primary human hepatocytes cultured for 5 days in the presence or absence of a Matrigel overlay. (A) Transcript levels for the hepatocyte differentiation markers, albumin, transferrin, and transthyretin, were assessed −/+ Matrigel additions using quantitative RT-PCR and the ΔΔCT method. (B) Transcript levels for the hepatocyte dedifferentiation markers, AFP and GSTPi, were similarly ascertained −/+ Matrigel additions and were normalized to each differentiation marker. (C) Primary human hepatocytes were cultured in the absence (control) or presence of Matrigel (MG). Cultures of primary human hepatocytes and HepG2 cells (indicated by arrows) were treated on day 4 with phenobarbital (PB and PB + MG) or left untreated (control) for 24 h prior to RNA isolation. Relative fold changes in transcript levels for the PB-inducible marker genes, CYP2B6 and CYP3A4, are indicated. (D) Total RNA was isolated from HepG2 cells, a section of human liver #154, as well as three different donor samples of primary human hepatocytes that were cultured with a Matrigel overlay. Relative expression analyses for a panel of differentiation and dedifferentiation markers were determined by quantitative RT-PCR analysis, and the results are graphically depicted.