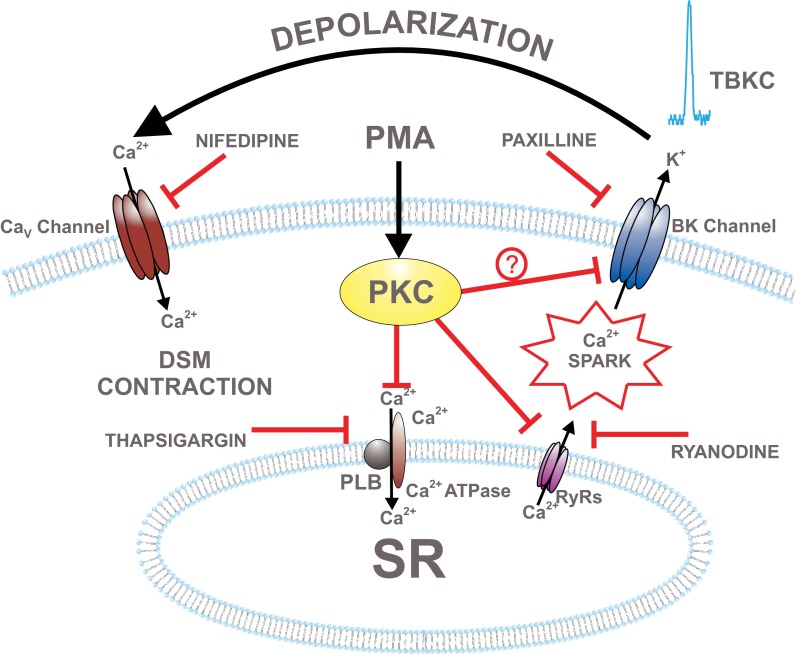
Fig. 8.
Schematic diagram illustrating proposed cellular mechanisms by which PKC regulates BK channel function in DSM. PMA activates PKC, which leads to inhibition of ryanodine receptors (RyRs) or sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ pump. This causes a decrease in Ca2+ spark and TBKC activity, leading to DSM cell membrane depolarization, L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ (CaV) channel activation, an increase in intracellular Ca2+, and DSM contraction. Pharmacological tools used in this study to inhibit cellular sources of Ca2+ are indicated. PLB, phospholamban.