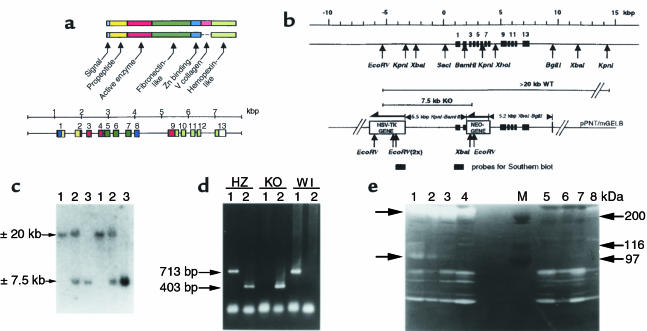
Figure 1.
Generation of gelatinase B–deficient mice. (a) Gelatinase A and B protein domain structure and gene organization of gelatinase B. Gelatinase B contains a type V collagen-like domain, not present in gelatinase A. Each domain is named, and a color code is used to indicate within the mouse genomic structure the exon parts that encode the respective protein domains. (b) Construction of targeting vector pPNT/mGEL-B. The sequence of the mouse gelatinase B gene (accession number X72794) was extended at the 5′- and 3′-ends, and fragments from the wild-type gene were used to generate the targeting vector pPNT/mGEL-B. Representative restriction sites for subcloning and analysis of wild-type or homologously recombined knockout genes are indicated. The scale bar indicates the fragment sizes in kbp. The orientation of the HSV-TK and NEO genes are antisense to the gelatinase B gene segments as indicated by the arrows. The localization of the 5′-end probes, used for Southern blot analysis, is indicated. (c) Genotyping by Southern blot analysis. Hybridization of EcoRV-digested tail DNA with a 5′-end probe resulted in bands of approximately 20 kb or 7.5 kb. Lanes 1 show the hybridization patterns of genomic DNA from wild-type mice, whereas lanes 2 are from heterozygote, and lanes 3 from gelatinase B–deficient, mice. (d) Screening by PCR analysis. Lanes 1 indicate the results of PCR, performed with a primer set to view the wild-type allele. Lanes 2 show the reaction products obtained with a knockout-specific primer set. The resulting genotype is indicated by heterozygous (HZ), knockout (KO), and wild-type (WT). The sizes of the amplified DNA-fragments are indicated in basepairs. (e) Functional analysis by zymography. Gelatinase activity was determined by SDS/PAGE gelatin substrate conversion. Lanes 1–4 show the analysis of leukocyte supernatants of 4 individual wild-type mice; lanes 5–8, those of 4 gelatinase B–deficient mice. The arrows indicate the gelatinase B zymolysis. Similar to control preparations of recombinant mouse gelatinase B, this zymolysis occurs mainly at >200 kDa (dimer, solid arrow), but also at the monomer position (110 kDa, arrowhead). M, molecular weight standardization.