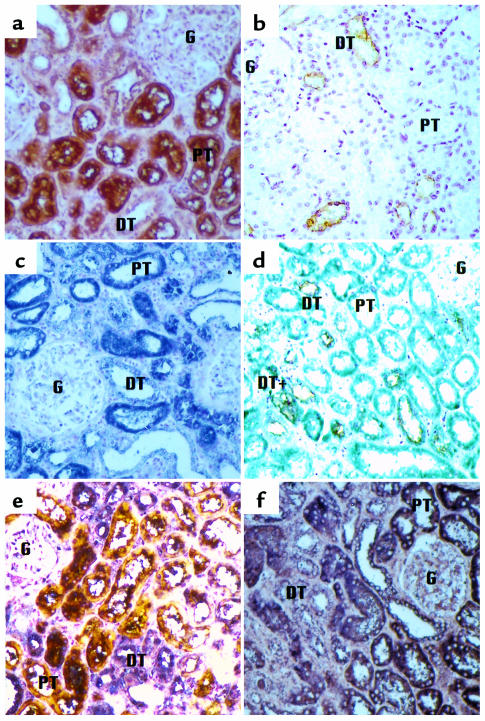
Figure 7.
Colocalization of CD21 and EBV DNA to proximal tubule cells in chronic idiopathic interstitial nephritis. (a) Treatment with peroxidase-labeled PHA-E lectin and a diaminobenzidine development system identifies proximal tubules as deep brown structures. (b) AH lectin identifies distal tubules by their yellow-brown appearance. (c) Immunohistochemical detection of CD21 using a specific antibody coupled to alkaline phosphatase with nitroblue tetrazolium as the detection reagent gives a purple color. (d and e) Sequential staining for CD21 by immunohistochemistry and lectin histochemistry for distal tubule (d) and for proximal tubule (e) identification. (f) ISH for EBV DNA followed by lectin histochemistry for proximal tubule identification. All sections are counterstained with nuclear fast red. G: glomerulus; PT: proximal tubule; DT: distal tubule. (×200).