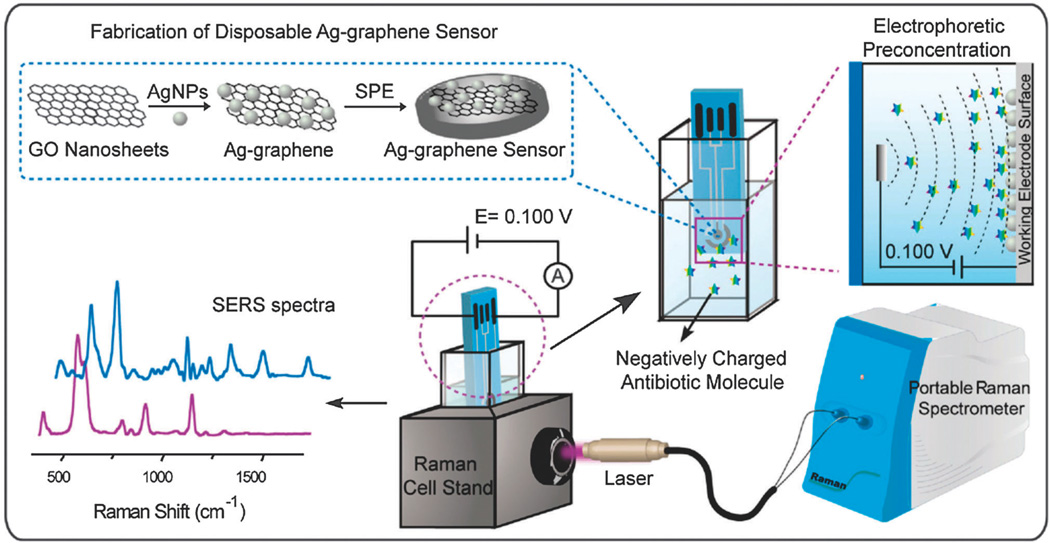
Fig. 8.
Schematic representation of a disposable Ag–graphene sensor for the detection of polar antibiotics in water. The magnification insets show the fabrication of Ag–graphene sensors and the electrophoretic preconcentration process of polar antibiotics. The distribution of antibiotics molecules is sketched for the case of a negatively charged analyte. At a given potential, most of the negatively charged antibiotics are concentrated onto the positively charged printed electrode, due to the generated electric field between the working electrode and the counter electrode. In SERS experiments, the laser comes vertically from the side view of the spectroelectrochemical cell and is focused on the Ag–graphene sensor. Reproduced from ref. 102 with permission from Elsevier.