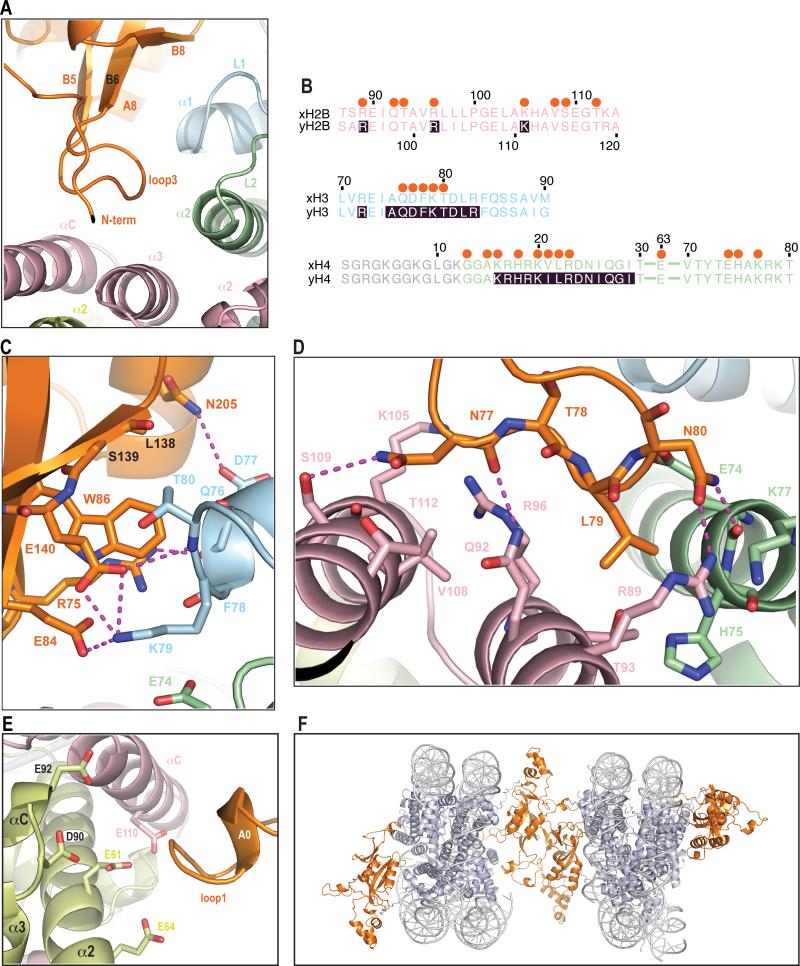
Figure 4. Interactions of BAH domain with a NCP body.
a) General view of interactions in this region.
Folded loop 3 and the β-strands that interact with regions of histones H3, H4 and H2B are shown.
b) Sequence alignment of regions of Xenopus and yeast histones (color coded the same as structure) that interact with BAH domain. Shaded residues were described in previous genetic screens. Orange spheres above the sequence depict which residues interact with BAH domain. The region of histone H4 that is disordered in the structure is depicted in grey.
c) Detailed interactions of BAH with H3.
A magnified view of a top part of panel a. Magenta dashes connect residues forming potential hydrogen bonds. Five LRS (Q76, D77, F78, K79 and T80) residues in helix α1 and loop L1 of H3 that contact the BAH domain in the structure. BAH W86 is within 4 Å of the H3Q76 carbonyl, T80 side chain and K79 Cα. There is a potential hydrogen bond between the H3D77 side chain carbonyl and the BAH N205 side chain amide. K79 could potentially form 3 hydrogen bonds with the BAH domain, one to the side chain of E84 and two to the E140 side chain. K79 conformation is further stabilized by van der Waals interactions with BAH W86 and H4E74. T80 side chain interacts with main chain of L138 and S139. BAH R75 forms polar interactions, one of which is a potential hydrogen bond with main chain of H3 residues D77 and F78. Additionally a hydrogen bond might also be formed between the BAH E140 side chain carbonyl and main chain amide of H3 T80.
d) Detailed interactions of BAH with H4 and H2B.
F78. Additionally a hydrogen bond might also be formed between the BAH
A magnified view of a bottom part of panel a. Magenta dashes connect residues forming potential hydrogen bonds. Two residues at the tip of loop 3 (L79 and N80) interact with histones H4 and histone H2B. They make van der Waals contacts with histone H4 residues E74, H75 and K77. Additionally the BAH N80 side-chain could form hydrogen bonds with main chain carbonyl of H4 E74 and side chain of H2B R89. L79 interacts with 3 H2B residues in helix a3 (R89, T93 and Q92). BAH N77 and T78 main chain carbonyls make charged interactions and a potential hydrogen bond with side-chains of H2B residues R96 and Q92, respectively. The side-chain of BAH N77 can additionally interact with four residues of H2B located in helix αC.
e) Interaction of the BAH domain with the acidic patch, same view as in Fig.1 (front).
A positively charged BAH patch (residues 28-34) is in close proximity to acidic residues E61, E64, D90 and E92 of H2A as well as residue E110 of H2B.
f) Crystal packing interaction.