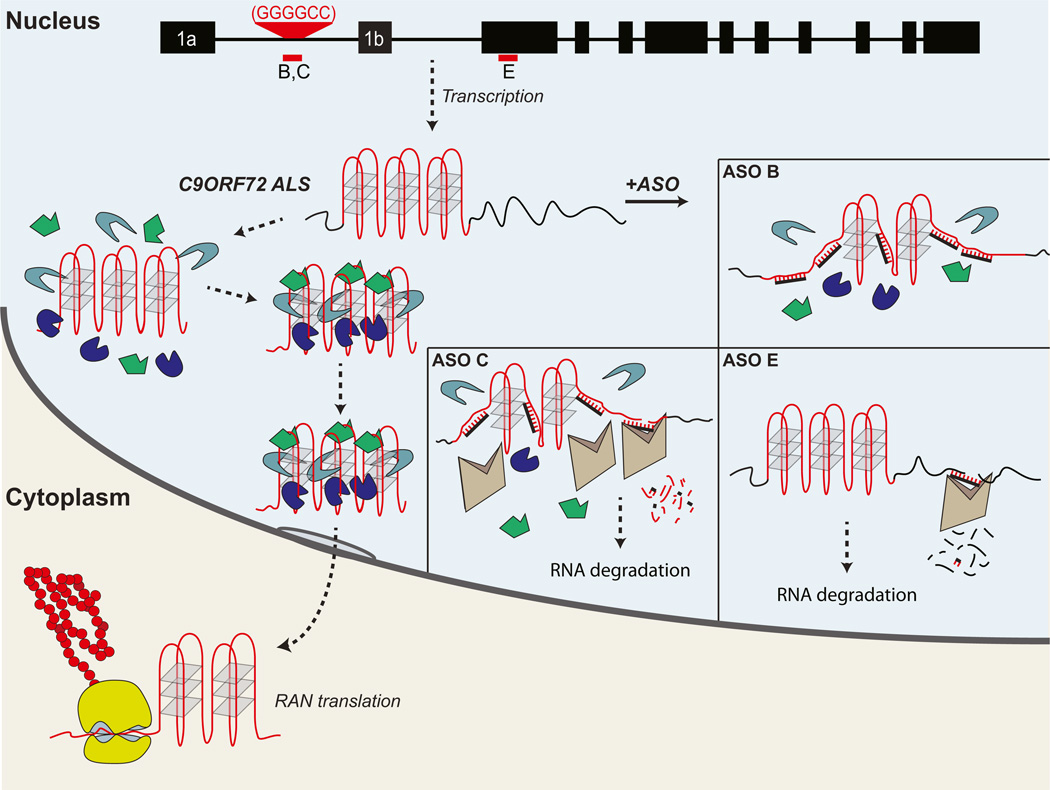
Figure 8. Pathogenesis Resulting from the C9ORF72 Noncoding GGGGCC Expansion in ALS/FTD.
Top. Representation of the human C9ORF72 gene, showing hexanucleotide expansion (red) and location of various antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) probes (B, C, E). Hexanucleotide expansion is located between the noncoding exons 1a and 1b. The expanded RNA is predicted to form a series of G-quartet tertiary structures. At least three different pathophysiological pathways may results from the mutation: (1) RNA toxicity resulting from excessive binding of various different RNA binding proteins (green, blue, gray polygons) leading to sequestration of these RBPs, and loss of their activity resulting in anomalous downstream events; (2) export of the expansion to cytoplasm with repeat-associated translation (RAN) (in the sense or antisense directions) and the formation of excessive high-molecular-weight cytoplasmic peptides (red), which may be toxic or protective; and (3) loss of C9ORF72 mRNA leading to loss of protein function (not shown). ASOs may disrupt C9ORF72 RNA toxicity by several pathways. ASO B: an endonuclease-resistant oligonucleotide that is predicted to disrupt the expansion, interfering with the G-quartet structure and preventing RBP interaction/sequestration. ASO C; a gapmer ASO that binds to the expansion targeting it RNase H-mediated cleavage and subsequent RNA degradation by nuclear endogenous nucleases, since this ASO targets the repeat it will also disrupt the repeat sequence structure prior to cleavage and prevent RBP sequestration. ASO E: a gapmer that targets the C9ORF72 RNA coding sequence marking the RNA for RNase H cleavage, thus resulting in the degradation of wild-type and the expanded C9ORF72 RNA; this will further reduce the already attenuated levels of cellular C9ORF72 RNA. Notably, ASOs B and C do not reduce cellular C9ORF72 RNA.