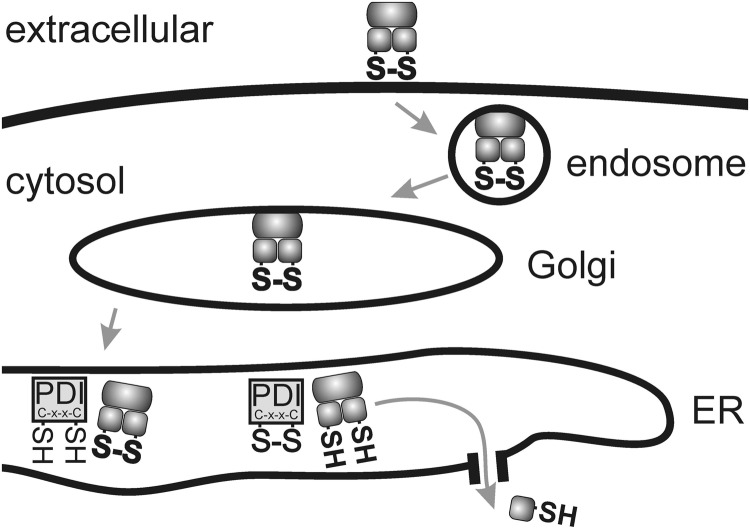
FIG. 8.
Retrograde transport followed by reductive translocation to the cytosol. Several protein toxins (e.g. Cholera toxin, Shiga toxin, Pertussis toxin, ricin, or Pseudomonas exotoxin A) attach to receptors on the surface of the cell and are transported via Golgi to the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) by retrograde transport. A key disulfide is recognized as a “misfolded ER substrate” and reduced in the presence of a protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) followed by translocation of a toxin fragment to the cytosol.