Figure 1.
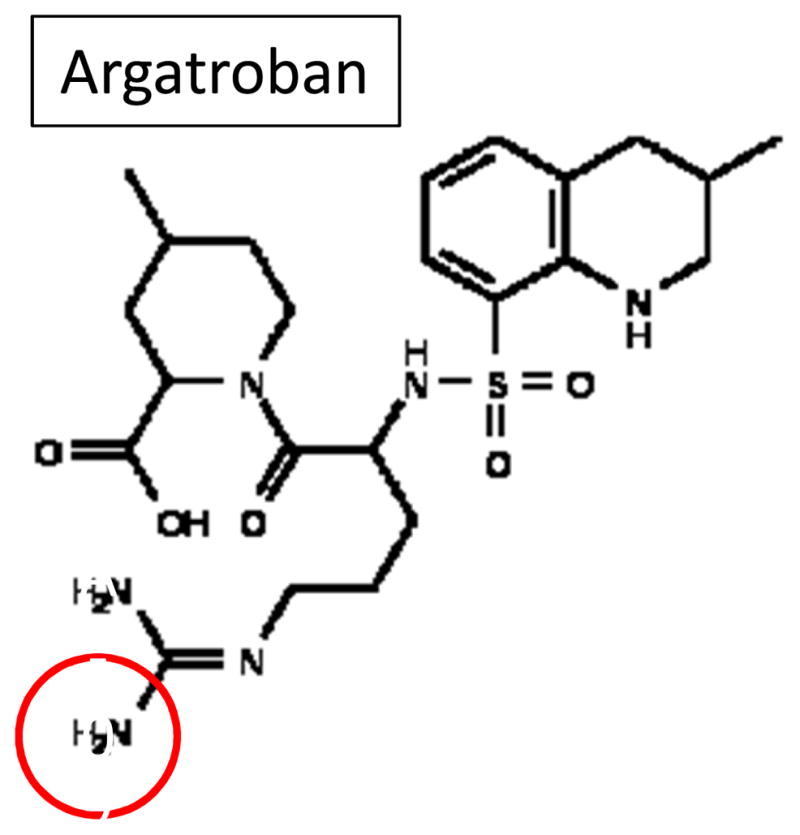
Structure of argatroban ((2R,4R)-1-[(2S)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-2-[[(3R)-3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl]sulfonylamino]pentanoyl]-4-methyl-piperidine-2-carboxylic acid). Chemically, argatroban (MW= 509) is the dipeptide between arginine and 4-methyl-2-piperidine carboxylic acid with the NH2 closest to the carbonyl group of arginine bonded to a methyltetrahydroquinoline sulfonyl group. The immobilization of argatroban was accomplished by linking the free primary amine of the arginine ‘tail’ to an isocyanate group of either HMDI or PEG-DI (red circle).
