Figure 3.
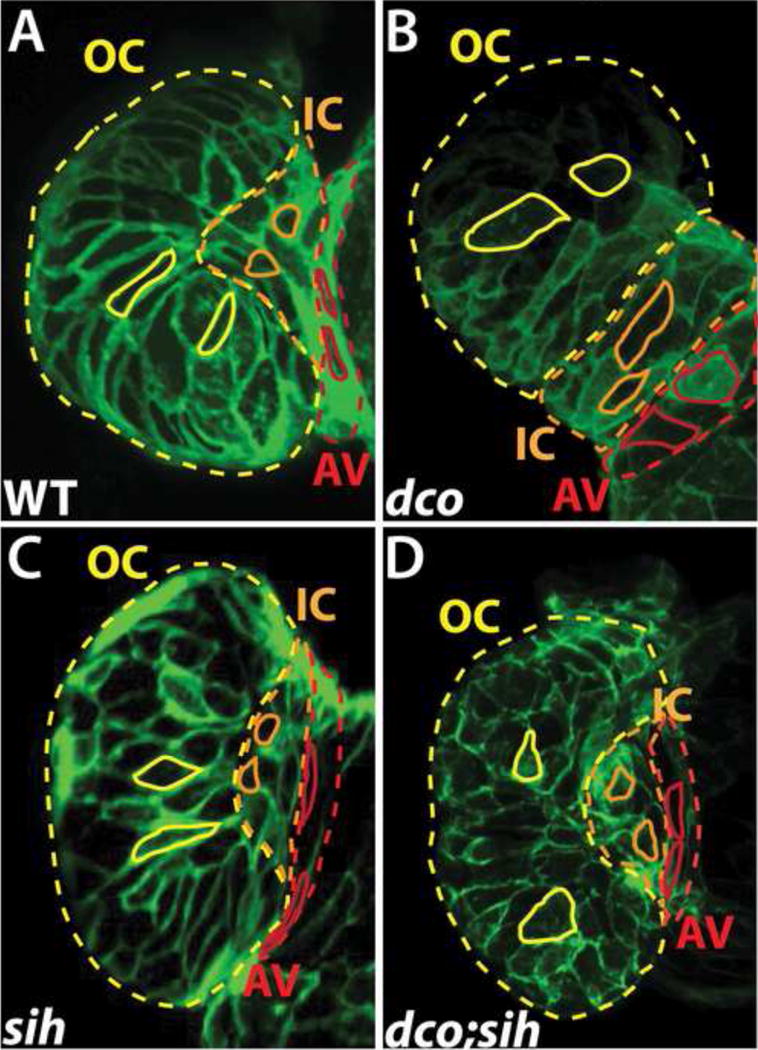
Cardiac conduction, independent of biomechanical forces, can influence cardiomyocyte morphogenesis. (A–D) Confocal images of the heart at 60 hpf, using Tg(cmlc2:ras-eGFP) to visualize the shape of individual cardiomyocytes in (A) wildtype (WT), (B) dco mutant (C) sih mutant, and (D) dco;sih double mutant. Solid yellow, orange, and red lines outline cardiomyocytes in the outer curvature (OC), inner curvature (IC), and atrioventricular canal (AV) of the ventricle, respectively. Dashed yellow, orange, and red lines outline the OC, IC and AV regions of the ventricle, respectively. Note ventricular OC cardiomyocytes in dco and dco;sih hearts are more circular compared to those in WT and sih hearts. [95]
